The impact of introducing multidisciplinary care assessments on access to rheumatology care in British Columbia: an interrupted time series analysis
- PMID: 35277162
- PMCID: PMC8915460
- DOI: 10.1186/s12913-022-07715-x
The impact of introducing multidisciplinary care assessments on access to rheumatology care in British Columbia: an interrupted time series analysis
Abstract
Background: In 2011 the British Columbia (BC) Ministry of Health introduced a new fee-for-service billing code that allowed "Multidisciplinary Care Assessment" (MCA). This change has the potential to change access to and quality of care for patients. This study aimed to explore the impact on access to rheumatology services in the province.
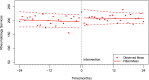
Methods: Fee-for-service rheumatology billings were evaluated for each rheumatologist 2 years before and after use of the MCA code. Numbers of 1) unique patients and 2) services provided per month were used as proxy measures of access to care. A multiple-baseline interrupted time series model assessed the impact of the MCA on levels and trends of the access outcomes.
Results: Our analysis consisted of 82,360 patients cared for by 26 rheumatologists who billed for an MCA. In our primary analysis we observed a sustained increase in the mean number of unique patients of 4.9% (95% CI: 0.0% to 9.9%, p = 0.049) and the mean number of services of 7.1% (95% CI: 1.0% to 13.6%, (p = 0.021), per month provided by a rheumatologist, corresponding to the initial use of MCA.
Conclusion: The introduction of the MCA code was associated with an initial increase in the measures of access, which was maintained but did not increase over time. Our study suggests that the use of Multidisciplinary Care Assessment can contribute to expanding and/or sustaining access to care for people with complex chronic conditions, like rheumatic diseases.
Keywords: Canada; Fee for service; Interrupted time series; Policy; Rheumatology.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Michael Law has consulted for Health Canada, the Health Employees’ Union, the Conference Board of Canada, and provided expert witness testimony for the Attorney General of Canada and the Federation of Post-secondary Educators. Dr Shojania is a rheumatologist who uses the G31060 “Multidisciplinary Care Assessment” billing code. All other authors report no competing interests.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Effect of a Billing Code to Reimburse Nurse-Supported Rheumatology Care on Health Care Costs and Access: An Interrupted Time Series Analysis.Arthritis Care Res (Hoboken). 2024 Jul;76(7):936-942. doi: 10.1002/acr.25317. Epub 2024 Mar 27. Arthritis Care Res (Hoboken). 2024. PMID: 38403453
-
Understanding multidisciplinary care for people with rheumatic disease in British Columbia, Canada, through patients, nurses and physicians voices: a qualitative policy evaluation.BMC Health Serv Res. 2021 Oct 23;21(1):1148. doi: 10.1186/s12913-021-07138-0. BMC Health Serv Res. 2021. PMID: 34688296 Free PMC article.
-
The Association of Rheumatologist Supply and Multidisciplinary Care With Timely Patient Access to Rheumatologists: Evidence From British Columbia, Canada.Arthritis Care Res (Hoboken). 2024 Apr;76(4):444-453. doi: 10.1002/acr.25274. Epub 2024 Feb 11. Arthritis Care Res (Hoboken). 2024. PMID: 38018333
-
Improving access to care for rheumatology services in Canada.Clin Rheumatol. 2023 Apr;42(4):1205-1211. doi: 10.1007/s10067-023-06532-9. Epub 2023 Feb 6. Clin Rheumatol. 2023. PMID: 36746833 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Workforce Trends in Rheumatology.Rheum Dis Clin North Am. 2019 Feb;45(1):13-26. doi: 10.1016/j.rdc.2018.09.002. Rheum Dis Clin North Am. 2019. PMID: 30447742 Review.
Cited by
-
Clinical Visit Frequencies in Rheumatology: A Systematic Literature Review.Arthritis Care Res (Hoboken). 2023 Oct;75(10):2054-2062. doi: 10.1002/acr.25106. Epub 2023 Mar 23. Arthritis Care Res (Hoboken). 2023. PMID: 36807719 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Siaw MYL, Lee JY-C. Multidisciplinary collaborative care in the management of patients with uncontrolled diabetes: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Int J Clin Pract. 2019;73(2):e13288. - PubMed
-
- Patel A, Jafferany M. Multidisciplinary and Holistic Models of Care for Patients With Dermatologic Disease and Psychosocial Comorbidity: A Systematic Review. JAMA Dermatol. 2020;156(6):686. - PubMed
-
- Wang S-M, Hsiao L-C, Ting I-W, Yu T-M, Liang C-C, Kuo H-L, et al. Multidisciplinary care in patients with chronic kidney disease: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Eur J Intern Med. 2015;26(8):640–645. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

