Microenvironmental stiffness mediates cytoskeleton re-organization in chondrocytes through laminin-FAK mechanotransduction
- PMID: 35277477
- PMCID: PMC8917190
- DOI: 10.1038/s41368-022-00165-5
Microenvironmental stiffness mediates cytoskeleton re-organization in chondrocytes through laminin-FAK mechanotransduction
Abstract
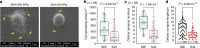
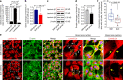
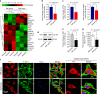
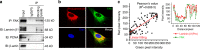
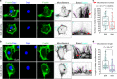
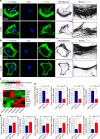
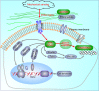
Microenvironmental biophysical factors play a fundamental role in controlling cell behaviors including cell morphology, proliferation, adhesion and differentiation, and even determining the cell fate. Cells are able to actively sense the surrounding mechanical microenvironment and change their cellular morphology to adapt to it. Although cell morphological changes have been considered to be the first and most important step in the interaction between cells and their mechanical microenvironment, their regulatory network is not completely clear. In the current study, we generated silicon-based elastomer polydimethylsiloxane (PDMS) substrates with stiff (15:1, PDMS elastomer vs. curing agent) and soft (45:1) stiffnesses, which showed the Young's moduli of ~450 kPa and 46 kPa, respectively, and elucidated a new path in cytoskeleton re-organization in chondrocytes in response to changed substrate stiffnesses by characterizing the axis shift from the secreted extracellular protein laminin β1, focal adhesion complex protein FAK to microfilament bundling. We first showed the cellular cytoskeleton changes in chondrocytes by characterizing the cell spreading area and cellular synapses. We then found the changes of secreted extracellular linkage protein, laminin β1, and focal adhesion complex protein, FAK, in chondrocytes in response to different substrate stiffnesses. These two proteins were shown to be directly interacted by Co-IP and colocalization. We next showed that impact of FAK on the cytoskeleton organization by showing the changes of microfilament bundles and found the potential intermediate regulators. Taking together, this modulation axis of laminin β1-FAK-microfilament could enlarge our understanding about the interdependence among mechanosensing, mechanotransduction, and cytoskeleton re-organization.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
References
-
- Engler AJ, Sen S, Sweeney HL, Discher DE. Matrix elasticity directs stem cell lineage specification. Cell. 2006;126:677–689. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

