Age-Dependent Reference Values for hs-Troponin T and NT-proBNP and Determining Factors in a Cohort of Healthy Children (The LIFE Child Study)
- PMID: 35277733
- PMCID: PMC8916935
- DOI: 10.1007/s00246-022-02827-x
Age-Dependent Reference Values for hs-Troponin T and NT-proBNP and Determining Factors in a Cohort of Healthy Children (The LIFE Child Study)
Abstract
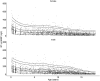
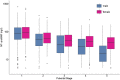
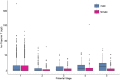
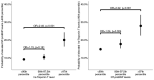
This study aimed to provide reliable pediatric reference values for N-terminal pro-brain natriuretic peptide (NT-proBNP) and high-sensitive Troponin T (hsTnT) obtained from a population of well children and investigate for associations with sex, pubertal status, body mass index (BMI), and serum lipid levels. We analyzed hsTnT and NT-proBNP values obtained from 4826 samples provided by 2522 children aged 0.25-18 years participating in a prospective longitudinal population-based cohort study, "LIFE child" in Leipzig, Germany (Poulain et al., Eur J Epidemiol 32:145-158, 2017). NT-proBNP values decreased throughout childhood from values over 400 ng/L at 3 months to 138 ng/L in females and 65 ng/L in males by 18 years of age. Values dropped rapidly with advancing pubertal stage. We found a strong association between lower NT-proBNP values and higher BMI or elevated serum lipids, the latter effect being more pronounced in males. For hsTnT levels, approximately half of the measurements were below the detection limit. However, 76% of those aged 3 months and 21% of those aged 6 months had values exceeding the adult cut-off limit. Females had slightly higher levels in the first 2 years of life but this was reversed during puberty. In males, there was an upward trend from pubertal stage 2 onward. We identified a positive association between hsTnT and BMI but a negative association with low-density lipoprotein (LDL) cholesterol and triglyceride levels in boys but not in girls. Based on a large number of healthy children, we have established reliable reference values for NT-proBNP and hsTnT for use in everyday clinical practice. We have also identified important associations between certain metabolic and cardiac markers.Clinical Trial Registration ClinicalTrial.gov (NCT02550236).
Keywords: Cardiac biomarkers; NT-ProBNP; Pediatric percentiles; Troponin T.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
All authors declare that they have no conflict of interest or financial ties to disclose.
Figures

References
-
- Valverde I, Singh Y, Sanchez-de-Toledo J, Theocharis P, Chikermane A, Di Filippo S, et al. Acute cardiovascular manifestations in 286 children with multisystem inflammatory syndrome associated with COVID-19 infection in Europe. Circulation. 2021;143:21–32. doi: 10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.120.050065. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Lam E, Higgins V, Zhang L, Chan MK, Bohn MK, Trajcevski K, et al. Normative values of high-sensitivity cardiac Troponin T and N-terminal pro-B-type natriuretic peptide in children and adolescents: a study from the CALIPER cohort. J Appl Lab Med. 2021;6:344–353. doi: 10.1093/jalm/jfaa090. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

