Antigenic and conserved peptides from diverse Helicobacter pylori antigens
- PMID: 35277779
- PMCID: PMC8916697
- DOI: 10.1007/s10529-022-03238-x
Antigenic and conserved peptides from diverse Helicobacter pylori antigens
Abstract
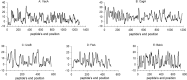
Since the revolutionary finding of Helicobacter pylori as a common bacterial infection, that a high research effort for its eradication has been conducted. Epitope based-vaccine presents advantages over protein-based, as they can be designed to contain epitopes from diverse proteins, therefore, more easily representing the immune-variability of the bacterial population, while minimizing the toxicity associated to some whole proteins. In the present work, an iterative method, to design antigenic and conserved B-epitopes from diverse virulent factors of H. pylori, was established. The method considered the trade-off between epitopes antigenicity and conservation among the bacterial population. For the method validation, five virulent factors from H. pylori were selected. From each virulent factor, two epitopes were predicted, each with twelve residues of aminoacids. The corresponding ten peptides were synthesised and evaluated by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay using polyclonal antibodies raised against a specific H. pylori strain. All ten peptides were recognised by the antibodies and were consequently antigenic and conserved. This result could strongly contribute to the design of a multivalent epitope-based vaccine, representing the immunogenetic variability within the bacterial population, leading to a sustained and effective immunogenic protection.
Keywords: Epitopes; Helicobacter pylori; Multi-antigens; Peptide; Vaccine.
© 2022. The Author(s), under exclusive licence to Springer Nature B.V.
Conflict of interest statement
The author declares that they have no conflict of interest.
Figures


References
-
- Ailloud F, Didelot X, Woltemate S, Pfaffinger G, Overmann J, Bader RC, Schulz C, Malfertheiner M, P, Suerbaum S, Within-host evolution of Helicobacter pylori shaped by niche-specific adaptation, intragastric migrations and selective sweeps. Nat Commun. 2019;10:2273. doi: 10.1038/s41467-019-10050-1. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

