An Introduction to Biosimilars for the Treatment of Retinal Diseases: A Narrative Review
- PMID: 35278204
- PMCID: PMC9114261
- DOI: 10.1007/s40123-022-00488-w
An Introduction to Biosimilars for the Treatment of Retinal Diseases: A Narrative Review
Abstract
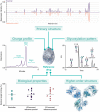
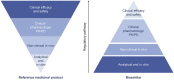
Biological therapies have revolutionized the treatment of disease across a number of therapeutic areas including retinal diseases. However, on occasion, such treatments may be relatively more expensive compared to small molecule therapies. This can restrict patient access and treatment length leading to suboptimal clinical outcomes. Several biosimilar candidates of ranibizumab and aflibercept are currently in development and the first biosimilar of ranibizumab received EMA approval in August and FDA approval in September 2021. Biosimilars are biological medicines that are highly similar to an already-approved biological medicine (reference product). The physicochemical and clinical similarity of a biosimilar is determined by a rigorous analytical and clinical program, including extensive pharmacokinetic and pharmacodynamic analysis with phase III equivalence studies where appropriate. These phase III studies are carried out in a patient population that is representative of all of the potential approved therapeutic indications of the originator product and the most sensitive for detecting potential differences between the biosimilar and the reference product. Biosimilars have been used successfully across a wide range of therapeutic areas for the past 15 years where they have achieved substantial cost savings that can be reinvested into healthcare systems without affecting the quality of patient care. The current review provides an introduction to biosimilars with the aim of preparing retinal specialists for discussing these products with their patients.
Keywords: Biologics; Biosimilars; Development; Extrapolation; Interchangeability; Retinal disease.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Figures

Similar articles
-
[Evolution of biologicals in inflammation medicine--biosimilars in gastroenterology, rheumatology and dermatology].Dtsch Med Wochenschr. 2014 Nov;139(47):2399-404. doi: 10.1055/s-0034-1387371. Epub 2014 Nov 12. Dtsch Med Wochenschr. 2014. PMID: 25390629 German.
-
Biosimilars in ulcerative colitis: When and for who?Best Pract Res Clin Gastroenterol. 2018 Feb-Apr;32-33:35-42. doi: 10.1016/j.bpg.2018.05.003. Epub 2018 May 26. Best Pract Res Clin Gastroenterol. 2018. PMID: 30060937 Review.
-
Biosimilars: impact of biologic product life cycle and European experience on the regulatory trajectory in the United States.Clin Ther. 2012 Feb;34(2):400-19. doi: 10.1016/j.clinthera.2011.12.005. Epub 2012 Jan 13. Clin Ther. 2012. PMID: 22244050 Review.
-
From bioequivalence to biosimilars: How much do regulators dare?Z Evid Fortbild Qual Gesundhwes. 2019 Mar;140:58-62. doi: 10.1016/j.zefq.2018.12.001. Epub 2019 Jan 6. Z Evid Fortbild Qual Gesundhwes. 2019. PMID: 30622000
-
Considerations related to comparative clinical studies for biosimilars.Expert Opin Drug Saf. 2021 Mar;20(3):265-274. doi: 10.1080/14740338.2021.1876024. Epub 2021 Feb 18. Expert Opin Drug Saf. 2021. PMID: 33455482
Cited by
-
One-Year Outcome of Intravitreal Injection of Ranibizumab Biosimilar for Myopic Choroidal Neovascularization in Japanese Patients.J Clin Med. 2024 Aug 8;13(16):4641. doi: 10.3390/jcm13164641. J Clin Med. 2024. PMID: 39200783 Free PMC article.
-
Clinical and Socioeconomic Burden of Retinal Diseases: Can Biosimilars Add Value? A Narrative Review.Ophthalmol Ther. 2025 Apr;14(4):621-641. doi: 10.1007/s40123-025-01104-3. Epub 2025 Feb 26. Ophthalmol Ther. 2025. PMID: 40009268 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Biosimilar SB15 versus reference aflibercept in neovascular age-related macular degeneration: 1-year and switching results of a phase 3 clinical trial.BMJ Open Ophthalmol. 2023 Dec 19;8(1):e001561. doi: 10.1136/bmjophth-2023-001561. BMJ Open Ophthalmol. 2023. PMID: 38114333 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Anti-vascular endothelial growth factor biosimilars for neovascular age-related macular degeneration.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2024 Jun 3;6(6):CD015804. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD015804.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2024. PMID: 38829176 Free PMC article.
-
Systematic review of efficacy and meta-analysis of safety of ranibizumab biosimilars relative to reference ranibizumab anti-VEGF therapy for nAMD treatment.BMJ Open Ophthalmol. 2023 Jun;8(1):e001205. doi: 10.1136/bmjophth-2022-001205. Epub 2023 Jun 15. BMJ Open Ophthalmol. 2023. PMID: 37493655 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Mao EJ, Hazlewood GS, Kaplan GG, Peyrin-Biroulet L, Ananthakrishnan AN. Systematic review with meta-analysis: comparative efficacy of immunosuppressants and biologics for reducing hospitalisation and surgery in Crohn's disease and ulcerative colitis. Aliment Pharmacol Ther. 2017;45(1):3–13. doi: 10.1111/apt.13847. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

