Differential T-Cell Immunity to Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) in mRNA-1273- and BNT162b2-Vaccinated Individuals
- PMID: 35278306
- PMCID: PMC9402689
- DOI: 10.1093/cid/ciac201
Differential T-Cell Immunity to Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) in mRNA-1273- and BNT162b2-Vaccinated Individuals
Abstract
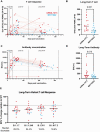
COVID-19 breakthrough cases among vaccinated individuals demonstrate the value of measuring long-term immunity to SARS-CoV-2 and its variants. We demonstrate that anti-spike T-cell responses and IgG antibody levels are maintained but decrease over time and are lower in BNT162b2- versus mRNA-1273-vaccinated individuals. T-cell responses to the variants are relatively unaffected.
Keywords: BNT162b2; SARS-CoV2 mRNA vaccine; T-cell immunity; T-cell response; mRNA-1273.
© The Author(s) 2022. Published by Oxford University Press for the Infectious Diseases Society of America. All rights reserved. For permissions, e-mail: journals.permissions@oup.com.
Figures
References
-
- Center for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC). Rates of COVID-19 cases and deaths by vaccination status. Available at: https://covid.cdc.gov/covid-data-tracker/#rates-by-vaccine-status. Accessed 8 November 2021.
-
- Guerrera G, Picozza M, D’Orso S, et al. . BNT162b2 vaccination induces durable SARS-CoV-2 specific T cells with a stem cell memory phenotype. Sci Immunol 2021: eabl5344. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Supplementary concepts
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

