Influence of menopause and hormone replacement therapy on epidermal ageing and skin biomechanical function
- PMID: 35279892
- PMCID: PMC9314060
- DOI: 10.1111/jdv.18071
Influence of menopause and hormone replacement therapy on epidermal ageing and skin biomechanical function
Conflict of interest statement
MB and VLN are employees of Walgreens Boots Alliance; REBW is in receipt of consultancy fees from Allergan Ltd.; CEMG is a Co‐Founder of CGSkincare Ltd.
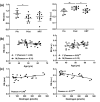
Figures

References
-
- LePillouer‐Prost A, Kerob D, Nielsen M et al. Skin and menopause: women's point of view. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol 2020; 34: e267–e269. - PubMed
-
- European Commission, Eurostat . In, Vol. Life Expectancy across European Regions. URL https://ec.europa.eu/eurostat/web/products‐eurostat‐news/‐/edn‐20200930‐1 (last accessed: 22 February 2021).
-
- Schmidt JB, Lindmaier A, Spona J. Hormone receptors in pubic skin of premenopausal and postmenopausal females. Gynecol Obstet Invest 1990; 30: 97–100. - PubMed
-
- Pelletier G, Ren L. Localization of sex steroid receptors in human skin. Histol Histopathol 2004; 19: 629–636. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

