The Effect of Pedaling at Different Cadence on Attentional Resources
- PMID: 35280213
- PMCID: PMC8913718
- DOI: 10.3389/fnhum.2022.819232
The Effect of Pedaling at Different Cadence on Attentional Resources
Abstract
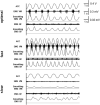
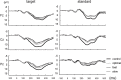
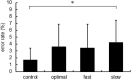
We investigated the relationship between attentional resources and pedaling cadence using electroencephalography (EEG) to measure P300 amplitudes and latencies. Twenty-five healthy volunteers performed the oddball task while pedaling on a stationary bike or relaxing (i.e., no pedaling). We set them four conditions, namely, (1) performing only the oddball task (i.e., control), (2) performing the oddball task while pedaling at optimal cadence (i.e., optimal), (3) performing the oddball task while pedaling faster than optimal cadence (i.e., fast), and (4) performing the oddball task while pedaling slower than optimal cadence (i.e., slow). P300 amplitudes at Cz and Pz electrodes under optimal, fast, and slow conditions were significantly lower than those under control conditions. P300 amplitudes at Pz under fast and slow conditions were significantly lower than those under the optimal condition. No significant changes in P300 latency at any electrode were observed under any condition. Our findings revealed that pedaling at non-optimal cadence results in less attention being paid to external stimuli compared with pedaling at optimal cadence.
Keywords: P300; attention; electroencephalography; oddball paradigm; pedaling.
Copyright © 2022 Akaiwa, Iwata, Saito, Shibata, Sasaki and Sugawara.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures



References
-
- Al-Yahya E., Dawes H., Smith L., Dennis A., Howells K., Cockburn J. (2011). Cognitive motor interference while walking: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Neurosci. Biobehav. Rev. 35 715–728. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

