Pharmacoeconomic evaluations of CDK4/6 inhibitors plus endocrine therapy for advanced hormone receptor-positive (HR+) and human epidermal growth factor receptor-2 negative (HER2-) breast cancer: a systematic review
- PMID: 35280368
- PMCID: PMC8908180
- DOI: 10.21037/atm-21-5110
Pharmacoeconomic evaluations of CDK4/6 inhibitors plus endocrine therapy for advanced hormone receptor-positive (HR+) and human epidermal growth factor receptor-2 negative (HER2-) breast cancer: a systematic review
Abstract
Background: Hormone receptor-positive (HR+) and human epidermal growth factor receptor-2 negative (HER2-) breast cancer is the most common molecular subtype of breast cancer in many countries, and endocrine therapy remains a mainstay in its treatment. Cyclin-dependent kinase (CDK) 4/6 inhibitors are a new class of targeted agents administered orally that are recommended being used in combination with endocrine therapy as first and second line treatments for advanced HR+/HER2- breast cancer. However, their high prices largely hinder using these drugs in real world settings. To offer a new basis for future research, we investigated the cost-effectiveness of combinations of CDK4/6 inhibitors with endocrine therapy in the treatment of advanced HR+/HER2- breast cancer.
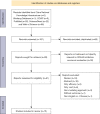
Methods: We systematically searched several frequently used databases and identified economic evaluations published from February 2015 to April 2021. The systematic review was performed after retrieving the literatures and extracting data based on inclusion and exclusion criteria. The quality of each selected economic evaluation was assessed by the Consolidated Health Economic Evaluation Reporting Standards (CHEERS).
Results: The literature search yielded 161 articles, among which fourteen studies (15 articles) with CHEER scores ranging from 58.33% to 87.50% entered the final analysis. Markov models were used in most studies. Based on the currently available data, CDK4/6 inhibitors plus endocrine therapy were less cost-effective in first- or second-line treatment of patients with HR+/HER2- advanced breast cancer. However, ribociclib plus letrozole was more cost-effective than palbociclib plus letrozole in the first-line treatment of postmenopausal women. The economic impacts of CDK4/6 inhibitors plus endocrine therapy in non-postmenopausal patients or second-line therapy cannot be fully evaluated due to the limited number of studies. The three most common factors affecting economic outcomes were the prices of CDK4/6 inhibitors, hazard ratios for progression-free survival and overall survival, and health status utility values.
Discussion: CDK4/6 inhibitors plus endocrine therapy have shown significantly improved efficacy outcomes in HR+/HER2- metastatic breast cancer (mBC)/advancer breast cancer (ABC) first-line and second-line treatment for endocrine-sensitive and endocrine-resistant populations, while more potential fields including neoadjuvant and adjuvant settings are being identified to benefit a wider range of breast cancer patients. Meanwhile, risk of severe adverse events that more likely to happen in patients treated with CDK4/6 inhibitors can lead to reduced life quality and higher medical costs patients need to afford. The adverse drug reaction related cost in several economic burden studies were explored to be primarily driven by hospitalizations and outpatient, and assessment of cost associated with CDK4/6 inhibitors adverse events is worth further developing. Drug wastage costs were found higher in palbociclib regimen than ribociclib regimen due to different dosing patterns. Moreover, current economic evaluations showed that ribociclib plus letrozole had better economic benefits than palbociclib plus letrozole for first-line treatment of postmenopausal women with HR+/HER2- ABC.
Keywords: CDK4/6 inhibitors; breast cancer; pharmacoeconomic evaluation; systematic review.
2022 Annals of Translational Medicine. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflicts of Interest: All authors have completed the ICMJE uniform disclosure form (available at https://atm.amegroups.com/article/view/10.21037/atm-21-5110/coif). The authors have no conflicts of interest to declare.
Similar articles
-
Cost-Effectiveness of Ribociclib plus Letrozole Versus Palbociclib plus Letrozole and Letrozole Monotherapy in the First-Line Treatment of Postmenopausal Women with HR+/HER2- Advanced or Metastatic Breast Cancer: A U.S. Payer Perspective.J Manag Care Spec Pharm. 2018 Jun;24(6):514-523. doi: 10.18553/jmcp.2018.24.6.514. J Manag Care Spec Pharm. 2018. PMID: 29799329 Free PMC article.
-
Cost Effectiveness of CDK4/6 Inhibitors in the First-Line Treatment of HR+/HER2- Metastatic Breast Cancer in Postmenopausal Women in the USA.Pharmacoeconomics. 2023 Jun;41(6):709-718. doi: 10.1007/s40273-023-01245-y. Epub 2023 Mar 15. Pharmacoeconomics. 2023. PMID: 36920662
-
Cost-effectiveness of ribociclib plus endocrine therapy versus placebo plus endocrine therapy in HR-positive, HER2-negative breast cancer.J Manag Care Spec Pharm. 2021 Mar;27(3):327-338. doi: 10.18553/jmcp.2021.27.3.327. J Manag Care Spec Pharm. 2021. PMID: 33645243 Free PMC article.
-
Association of Cyclin-Dependent Kinases 4 and 6 Inhibitors With Survival in Patients With Hormone Receptor-Positive Metastatic Breast Cancer: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis.JAMA Netw Open. 2020 Oct 1;3(10):e2020312. doi: 10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2020.20312. JAMA Netw Open. 2020. PMID: 33048129 Free PMC article.
-
The Growing Role of CDK4/6 Inhibitors in Treating Hormone Receptor-Positive Advanced Breast Cancer.Curr Treat Options Oncol. 2017 Jan;18(1):6. doi: 10.1007/s11864-017-0443-7. Curr Treat Options Oncol. 2017. PMID: 28197838 Review.
Cited by
-
A population‑based propensity score matching analysis of neoadjuvant compared to adjuvant chemotherapy in luminal breast cancer.Sci Rep. 2025 Mar 20;15(1):9568. doi: 10.1038/s41598-025-93934-1. Sci Rep. 2025. PMID: 40113956 Free PMC article.
-
The expression of epidermal growth factor receptor 2 and its relationship with tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes and clinical pathological features in breast cancer patients.Open Life Sci. 2025 Jul 15;20(1):20251113. doi: 10.1515/biol-2025-1113. eCollection 2025. Open Life Sci. 2025. PMID: 40678390 Free PMC article.
-
Intrinsic subtypes and therapeutic decision-making in hormone receptor-positive/HER2-negative metastatic breast cancer with visceral crisis: A case report.Front Oncol. 2022 Nov 8;12:1009352. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2022.1009352. eCollection 2022. Front Oncol. 2022. PMID: 36425558 Free PMC article.
-
Novel Therapeutic Combination Targets the Growth of Letrozole-Resistant Breast Cancer through Decreased Cyclin B1.Nutrients. 2023 Mar 28;15(7):1632. doi: 10.3390/nu15071632. Nutrients. 2023. PMID: 37049472 Free PMC article.
-
Comparative cost-effectiveness analysis of CDK4/6 inhibitors in the first-line treatment of HR-positive and HER2-negative advanced breast cancer: a Markov's model-based evaluation.Front Oncol. 2024 Jul 24;14:1413676. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2024.1413676. eCollection 2024. Front Oncol. 2024. PMID: 39114308 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous