Efficacy of systematic voice training combined with swallowing function exercises for the prevention of swallowing dysfunction in stroke patients: a retrospective study
- PMID: 35280372
- PMCID: PMC8908138
- DOI: 10.21037/atm-22-101
Efficacy of systematic voice training combined with swallowing function exercises for the prevention of swallowing dysfunction in stroke patients: a retrospective study
Abstract
Background: Stroke is a common clinical brain disease, and swallowing dysfunction is one of the most common complications in stroke patients. Despite multiple treatments for swallowing dysfunction, it often leads to a series of complications. Interventions such as systematic voice training and swallowing function exercises have emerged in recent years, but their effectiveness remains unclear. Therefore, this study was conducted to investigate the effect of systematic voice training combined with swallowing function exercise for the prevention of swallowing dysfunction and improving the quality of life of stroke patients.
Methods: We retrospectively analyzed 90 stroke patients admitted to Baotou Central Hospital from October 2018 to October 2021 as study subjects, and divided the patients into a combined voice training group (n=45) and a single swallowing exercise group (n=45) according to the interventions. The single swallowing exercise group received routine swallowing function exercise, and the combined voice training group used systematic voice training combined with swallowing function exercise. The incidence of swallowing dysfunction, malnutrition, aspiration pneumonia, and exercise compliance rate were compared between the two groups, and the quality of life of the two groups was evaluated by the Generic Quality of Life Inventory 74 (GQOLI-74) before and after the interventions, respectively.
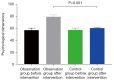
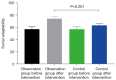
Results: The incidence of swallowing dysfunction, aspiration pneumonia, and malnutrition were lower in the combined voice training group than in the single swallowing exercise group (P<0.05), and there was no statistically significant difference in the exercise compliance rate between the two groups. The combined voice training group had higher psychological dimensions, physical dimensions, social adaptation, and total quality of life scores than the single swallowing exercise group (all P<0.05). Compared with the conventional intervention group, the combined voice training group had higher patient satisfaction (P<0.05).
Conclusions: Systematic voice training combined with swallowing function exercise can effectively prevent the occurrence of swallowing dysfunction and improve the quality of life of patients with stroke.
Keywords: Stroke; swallowing dysfunction; swallowing function exercise; systematic voice training.
2022 Annals of Translational Medicine. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflicts of Interest: All authors have completed the ICMJE uniform disclosure form (available at https://atm.amegroups.com/article/view/10.21037/atm-22-101/coif). The authors have no conflicts of interest to declare.
Figures


References
-
- Hao H, Bai JY, Li L, et al. Analysis on the effect of voice training and voice hygiene education in the treatment of vocal nodule. Chin J Otorhinolaryngol Integ Med 2019;27:268-71.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
