SENP1 inhibition suppresses the growth of lung cancer cells through activation of A20-mediated ferroptosis
- PMID: 35280420
- PMCID: PMC8908163
- DOI: 10.21037/atm-21-6909
SENP1 inhibition suppresses the growth of lung cancer cells through activation of A20-mediated ferroptosis
Abstract
Background: Ferroptosis is a type of cell death driven by iron accumulation and lipid peroxidation, which is involved in the pathogenesis of various tumors. Small ubiquitin-like modifier (SUMO)-specific protease 1 (SENP1) is a critical SUMO-specific protease, which controls multiple cellular signaling processes. However, the roles and mechanisms of SENP1-mediated protein SUMOylation in the regulation of cell death and ferroptosis remain unexplored.
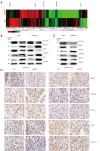
Methods: The gene expression of SENP1 and ferroptosis-related genes in samples of lung cancer patient and cells were determined by immunohistochemical staining, real-time polymerase chain reaction (RT-qPCR) and Western blot. The association of gene expression with the survival rate of lung cancer patients was analyzed from public database. The erastin and cisplatin was used to induce ferroptosis, and cell ferroptosis were determined by evaluated lipid-reactive oxygen species (ROS), cell viability and electron microscopy. The protein interaction was determined by immunoprecipitation (IP) and shotgun proteomics analysis. An in vivo tumor transplantation model of immunodeficient mice was used to evaluate the effect of SENP1 on tumor growth in vivo.
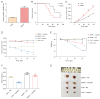
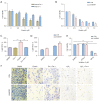
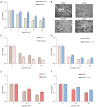
Results: SENP1 is aberrantly overexpressed in lung cancer cells and is associated with the low survival rate of patients. SENP1 inhibition by short hairpin RNA transduction or a specific inhibitor suppressed the proliferation and growth of lung cancer cells both in vitro and in vivo. SENP1 overexpression protected lung cancer cells from ferroptosis induced by erastin or cisplatin. Transcriptome and proteomics profiles revealed the involvement of SUMOylation regulation of the inflammation signal A20 in SENP1 inhibition-induced ferroptosis. Functional studies proved that A20 functions as a positive inducer and enhances the ferroptosis of A549 cells. A20 was shown to interact with ACSL4 and SLC7A11 to regulate the ferroptosis of lung cancer cells.
Conclusions: SENP1 was identified as a suppressor of ferroptosis through a novel network of A20 SUMOylation links ACSL4 and SLC7A11 in lung cancer cells. SENP1 inhibition promotes ferroptosis and apoptosis and represents a novel therapeutic target for lung cancer therapy.
Keywords: A20; Lung cancer; SENP1; ferroptosis; target therapy.
2022 Annals of Translational Medicine. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflicts of Interest: All authors have completed the ICMJE uniform disclosure form (available at https://atm.amegroups.com/article/view/10.21037/atm-21-6909/coif). The authors have no conflicts of interest to declare.
Figures





Similar articles
-
SENP1 inhibits ferroptosis and promotes head and neck squamous cell carcinoma by regulating ACSL4 protein stability via SUMO1.Oncol Rep. 2024 Feb;51(2):34. doi: 10.3892/or.2023.8693. Epub 2024 Jan 8. Oncol Rep. 2024. PMID: 38186303 Free PMC article.
-
miRNA-17-92 protects endothelial cells from erastin-induced ferroptosis through targeting the A20-ACSL4 axis.Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2019 Jul 30;515(3):448-454. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2019.05.147. Epub 2019 May 31. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2019. PMID: 31160087
-
Hypoxia protects H9c2 cells against Ferroptosis through SENP1-mediated protein DeSUMOylation.Int J Med Sci. 2021 Feb 4;18(7):1618-1627. doi: 10.7150/ijms.50804. eCollection 2021. Int J Med Sci. 2021. PMID: 33746578 Free PMC article.
-
Ferroptosis: process and function.Cell Death Differ. 2016 Mar;23(3):369-79. doi: 10.1038/cdd.2015.158. Epub 2016 Jan 22. Cell Death Differ. 2016. PMID: 26794443 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Emerging role of SENP1 in tumorigenesis and cancer therapy.Front Pharmacol. 2024 Feb 8;15:1354323. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2024.1354323. eCollection 2024. Front Pharmacol. 2024. PMID: 38389923 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Targeting epigenetic and posttranslational modifications regulating ferroptosis for the treatment of diseases.Signal Transduct Target Ther. 2023 Dec 10;8(1):449. doi: 10.1038/s41392-023-01720-0. Signal Transduct Target Ther. 2023. PMID: 38072908 Free PMC article. Review.
-
SENP1-mediated deSUMOylation of YBX1 promotes colorectal cancer development through the SENP1-YBX1-AKT signaling axis.Oncogene. 2025 May;44(19):1361-1374. doi: 10.1038/s41388-025-03302-6. Epub 2025 Feb 23. Oncogene. 2025. PMID: 39988696 Free PMC article.
-
Dissecting the dual role of OTU family proteins in tumor progression and immune escape.Front Immunol. 2025 May 21;16:1544341. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2025.1544341. eCollection 2025. Front Immunol. 2025. PMID: 40469292 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Targeting ferroptosis: a promising approach for treating lung carcinoma.Cell Death Discov. 2025 Jan 29;11(1):33. doi: 10.1038/s41420-025-02308-z. Cell Death Discov. 2025. PMID: 39875356 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Targeting Ferroptosis by Ubiquitin System Enzymes: A Potential Therapeutic Strategy in Cancer.Int J Biol Sci. 2022 Aug 29;18(14):5475-5488. doi: 10.7150/ijbs.73790. eCollection 2022. Int J Biol Sci. 2022. PMID: 36147464 Free PMC article. Review.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
