Identification of key biomarkers and immune infiltration in renal interstitial fibrosis
- PMID: 35280428
- PMCID: PMC8908133
- DOI: 10.21037/atm-22-366
Identification of key biomarkers and immune infiltration in renal interstitial fibrosis
Abstract
Background: Renal interstitial fibrosis (RIF) is the common final pathway that mediates almost all progressive renal diseases. However, the underlying mechanisms of RIF have not been fully elucidated. Therefore, the current study aimed to explore the etiology of RIF and identify the key targets and immune infiltration patterns of RIF.
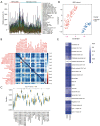
Methods: Ribonucleic acid (RNA)-seq data of RIF and normal samples were downloaded from the Gene Expression Omnibus (GEO) database. Weighted gene co-expression network analysis (WGCNA) was performed to screen relevant modules associated with RIF. Differentially expressed genes (DEGs) between the RIF and normal samples were identified using the limma package. Machine learning methods were used to identify hub gene signatures related to RIF. Further biochemical approaches including quantitative polymerase chain reaction (qPCR), immunoblotting and immunohistochemistry experiments were performed to verify the hub signatures in the RIF samples. Single sample gene set enrichment analysis (ssGSEA) was used to analyze the proportions of 28 immune cells in RIF and normal samples.
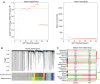
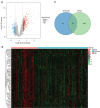
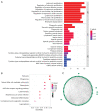
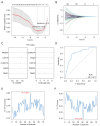
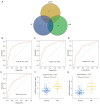
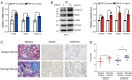
Results: WGCNA showed 121 RIF-related genes. A total of 523 DEGs were found between the RIF and normal samples. By overlapping these genes, we obtained 78 RIF-related genes, which were mainly enriched in Gene Ontology (GO) and Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes (KEGG) pathways associated with immunity and inflammation. Integrative analysis of machine learning methods showed prominin 1 (PROM1), tryptophan aspartate-containing coat protein (CORO1A), interferon-stimulated exonuclease gene 20 (ISG20), and tissue inhibitor matrix metalloproteinase 1 (TIMP1) as hub gene signatures in RIF. Further, receiver operating curve (ROC) curves implied the diagnostic role of ISG20 and CORO1A in RIF. The expression levels of ISG20 and CORO1A were significantly higher in fibrotic tubular cells and renal tissues based on biochemical approaches. The immune microenvironment was found to be markedly altered in the RIF samples, as 21 differentially infiltrated immune cells (DIICs) were found between RIF and normal samples.
Conclusions: This study is the first to find that ISG20 and CORO1A are key biomarkers and to examine the landscape of immune infiltration in RIF. Our findings provide novel insights into the mechanisms and treatment of patients with RIF.
Keywords: CORO1A; ISG20; Renal interstitial fibrosis (RIF); immune infiltration; machine learning.
2022 Annals of Translational Medicine. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflicts of Interest: All authors have completed the ICMJE uniform disclosure form (available at https://atm.amegroups.com/article/view/10.21037/atm-22-366/coif). The authors have no conflicts of interest to declare.
Figures
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
