Augmented reality 3D navigation system for percutaneous CT-guided pulmonary ground-glass opacity biopsies: a comparison with the standard CT-guided technique
- PMID: 35280488
- PMCID: PMC8902131
- DOI: 10.21037/jtd-21-1285
Augmented reality 3D navigation system for percutaneous CT-guided pulmonary ground-glass opacity biopsies: a comparison with the standard CT-guided technique
Abstract
Background: Augmented reality navigation system for percutaneous computed tomography (CT)-guided pulmonary biopsies has recently been introduced. There are no studies in literature about its use for ground glass lesions biopsies. The aim of this study is to evaluate the effectiveness of an augmented reality infrared navigation system performance on CT-guided percutaneous lung ground glass opacity (GGO) biopsy compared to a standard CT-guided technique.
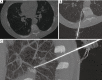
Methods: A total of 80 patients with lung GGO who underwent to a percutaneous CT-guided lung biopsy with an augmented reality infrared navigation system were retrospectively enrolled in the study. Comparison was performed with a group of 80 patients who underwent to lung biopsy with the standard CT-guided technique. Evaluation of maximum lesion diameter (MLD), distance between lesion and pleural surface (DPS), distance travelled by the needle (DTP), procedural time, validity of histological sample, procedural complications and the radiation dose to the patient's chest were recorded for each patient of both groups. In addition, each group was divided into two subgroups based on lesion size, according to a cut-off of 1.5 cm (<1.5 cm; ≥1.5 cm).
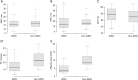
Results: Augmented reality navigation system showed a significant reduction in procedural time, radiation dose administrated to patients and complications rate compared to a standard CT-guided technique. Technical success was achieved in the 100% of cases in both groups, but the diagnostical success was higher in the group where patients underwent to lung biopsies with the use of navigation system. We also found that using an augmented reality navigation system increases the diagnostical success rate for lesion <1.5 cm. MLD, DPS and DTP did not differ significantly between the two groups of patients.
Conclusions: The use of an augmented reality navigation system for percutaneous CT-guided pulmonary GGO biopsies has demonstrated a lower incidence of post-procedural complications, a significantly reduction of the radiation dose administered to patients and a higher diagnostical success rate.
Keywords: Ground glass opacity (GGO); augmented reality navigation system; percutaneous lung biopsy (PLB).
2022 Journal of Thoracic Disease. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflicts of Interest: All authors have completed the ICMJE uniform disclosure form (available at https://jtd.amegroups.com/article/view/10.21037/jtd-21-1285/coif). PC serves as an unpaid editorial board member of Journal of Thoracic Disease from November 2016 to October 2022. The other authors have no conflicts of interest to declare.
Figures


References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
