Marsdenia tenacissima Extract Induces Autophagy and Apoptosis of Hepatocellular Cells via MIF/mToR Signaling
- PMID: 35280512
- PMCID: PMC8916871
- DOI: 10.1155/2022/7354700
Marsdenia tenacissima Extract Induces Autophagy and Apoptosis of Hepatocellular Cells via MIF/mToR Signaling
Abstract
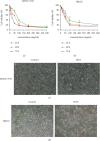
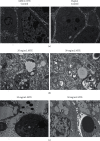
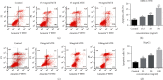
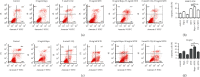
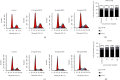
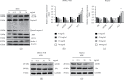
Hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) seriously endangers humans. In traditional Chinese medicine, Marsdenia tenacissima (MTE) has anti-inflammatory, antiasthmatic, antihypertensive, and anticancer effects. This study reveals the antiproliferative effect of MTE on the HCC cells in vitro and provides a theoretical basis for the development and clinical application of anti-HCC agents. Methods. MHCC-97H and HepG2 cells were cultured in vitro and exposed to various concentrations and durations of MTE, and an MTT assay was used to detect the effects of MTE on cell proliferation. Transmission electron microscopy revealed the morphological changes in the two cell lines after MTE stimulation. The MTE effects on the apoptosis and cell cycle distribution of the cell lines were detected by flow cytometry. Western blotting and qRT-PCR were used to detect target gene expression at the protein and mRNA levels, respectively. Results. MTE reduced the viability of the MHCC-97H and HepG2 cells in a dose- and time-dependent manners (P < 0.05). Autophagic vesicles and apoptotic bodies were found in the MHCC-97H and HepG2 cells after MTE incubation, and the Annexin V-PI assay showed that the apoptotic rates of the cell lines increased with increasing MTE concentration (P < 0.05). Autophagy inducer rapamycin promoted the MTE-induced apoptotic rates of the cell lines, whereas autophagy inhibitor chloroquine inhibited the apoptotic rates. More cells in the S phase were found in the two cell lines after MTE treatment (P < 0.05). After MTE incubation, MIF, CD47, and beclin-1 protein levels significantly increased. Furthermore, in the MTE group, Akt, mTOR, and caspase3 expressions decreased; however, LC 3 expression increased, which was significantly different from the control group (P < 0.05). Conclusions. MTE inhibited proliferation and induced autophagy, apoptosis, and S phase cell cycle arrest in the MHCC-97H and HepG2 cells. These effects might be related to the activation of MIF and mTOR signaling inhibition.
Copyright © 2022 Shuai Lin et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Ronot M., Bouattour M., Wassermann J., et al. Alternative response criteria (Choi, European association for the study of the liver, and modified Response Evaluation Criteria in Solid Tumors [RECIST]) versus RECIST 1.1 in patients with advanced hepatocellular carcinoma treated with sorafenib. The Oncologist . 2014;19(4):394–402. doi: 10.1634/theoncologist.2013-0114. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Asafo-Agyei K. O., Samant H. Hepatocellular Carcinoma . Treasure Island, FL, USA: StatPearls Publishing LLC.; 2020. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

