Deciphering chemical profiling, pharmacological responses and potential bioactive constituents of Saussurea lappa Decne. Extracts through in vitro approaches
- PMID: 35280548
- PMCID: PMC8913551
- DOI: 10.1016/j.sjbs.2022.01.040
Deciphering chemical profiling, pharmacological responses and potential bioactive constituents of Saussurea lappa Decne. Extracts through in vitro approaches
Abstract
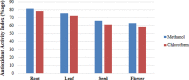
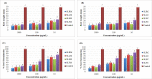
Despite advancement in modern medicines, plant derived medicines have still wide range utilities as they have less side effects and are cheap and biocompitable. Sassurea lappa is an extensively used plant in traditional medicinal formulations. Plant roots are used to cure various diseases including cancer, rheumatic pain, abdominal and nervous disorders. The present study was aimed for the evalution of biological potentials of methanolic and chloroform extracts of Saussurea lappa root, leaf, seed and flower. The methanolic and chloroform extracts were subjected to qualitative and quantitative phytochemical analyses. Identification of functional groups was performed using Fourier Transform infrared (FT-IR) spectroscopy. Antioxidant potential was determined via diphenyl-1-picrylhydrazyl (DPPH), total reducing power (TRP) and total antioxidant capacity (TAC) method, anti-hemolytic potential was conducted on human RBCs, antibacterial activity was evaluated against six American type culture collection (ATCC) and three multi drug resistance (MDR) strains, cytotoxic and phytotoxic potentials were evaluated through brine shrimp lethality assay and raddish seed assay respectively. Experiments were performed in triplicates and analysis of variance (ANOVA) was applied using statistics version-8.1. Phytochemical analysis revealed the presence of sixteen secondary metabolites. Fourteen functional groups were identified through FTIR. S. lappa root methanolic (SLRM) showed maximum antioxidant activity index (AAI-79.42%) whereas chloroform extract of leaves (SLLC) gave highest antibacterial activity with maximum zone of inhibition (ZOI) against Pseudomonas aeruginosa (21.4 mm). Maximum cytotoxicity was observed for SLRM with lethal dose concentration (LC50) of 58.8 µg/mL. However, root extracts showed significant phytotoxicity (15% germination). The current study investigated that bioactive compounds present in S. lappa leaves, seed, flower and roots were responsible for enhanced biological potentials. Further studies on isolation and characterization of these bioactive compounds may help in drug development. In future, we recommend different in-vitro and in-vivo studies to further confirm it biopharmacological potencies.
Keywords: Anti-hemolytic; Antibacterial; Antioxidant; Cytotoxic; S. lappa.
© 2022 The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures





References
-
- Adnan Q., Akhtar N., Ali Khan B. Phytoformulation of Saussurea lappa plant extract: A single blind, non-invasive and split face study of cream on various skin parameters. Pak. J. Pharm Sci. 2017;30 - PubMed
-
- Ajuru M.G., Williams L.F., Ajuru G. Qualitative and quantitative phytochemical screening of some plants used in ethnomedicine in the Niger Delta region of Nigeria. J. Food Nutr. Sci. 2017;5(5):198–205.
-
- Al Otibi F., Rizwana H., Alharbi R.I., Alshaikh N., Albasher G. Antifungal Effect of Saussurea lappa Roots Against Phytopathogenic Fungi and Resulting Morphological and Ultrastructural ChangesFungizide Wirkung von Saussurea lappa-Wurzeln gegen phytopathogene Pilze und resultierende morphologische und ultrastrukturelle Veränderungen. Gesunde Pflanzen. 2020;72(1):57–67.
-
- Ali S., Khan M.R., Iqbal J., Shah S.A., Abbasi B.A., Yaseen T., Batool R., Ali I., Hussain M.D., Kazi M. Chemical characterization and evaluation of the nephroprotective potential of Parrotiopsis jacquemontiana (Decne) Rehder and Periploca hydaspidis Falc crude extract in CCl4-induced Male Sprague-Dawley Rats. Saudi Journal of Biological Sciences. 2021 doi: 10.1016/j.sjbs.2021.09.057. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Further Reading
-
- Uttra A.M., Ahsan H., Hasan U.H., Chaudhary M.A. Traditional medicines of plant origin used for the treatment of inflammatory disorders in Pakistan: a review. J. Tradit. Chin. Med. 2018;38(4):636–656. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

