Predicting depression among the elderly by stressful life events and coping strategies
- PMID: 35280628
- PMCID: PMC8884286
- DOI: 10.4103/jfmpc.jfmpc_881_21
Predicting depression among the elderly by stressful life events and coping strategies
Abstract
Background and aim: Aging is a stage during which stressful events occur frequently. The method of coping with this stress can play an important role in an elderly's mental health. The present study aimed at investigating the role of coping strategies in stressful life events associated with depression.
Method: The present study was a correlational one conducted by structural equation analysis. As many as 841 elderly people were selected from the general population by adopting a cluster sampling method. Beck's Depression Inventory as well as strategies of coping with stress and stressful events were applied.
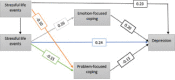
Results: The model test, analyzed by AMOS by using path analysis, indicated that age is positively associated with stressful life events and depression. The "stressful life events" variable is directly and indirectly associated with depression. The emotion-focused coping strategies were positively associated with depression, and problem-focused coping strategies were negatively associated with depression.
Conclusion: As an individual grows older and experiences stressful life events, his/her depression increases. Elderly people with problem-focused coping strategies are likely to experience less depression.
Keywords: Aging; coping strategies; depression; stressful life events.
Copyright: © 2021 Journal of Family Medicine and Primary Care.
Conflict of interest statement
There are no conflicts of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Mediation by coping style in the association between stressful life events and depressive symptoms in young adults.Soc Psychiatry Psychiatr Epidemiol. 2022 Dec;57(12):2401-2409. doi: 10.1007/s00127-022-02341-8. Epub 2022 Jul 27. Soc Psychiatry Psychiatr Epidemiol. 2022. PMID: 35895096
-
Stressful events and coping strategies associated with symptoms of depression: A Japanese general population survey.J Affect Disord. 2018 Oct 1;238:482-488. doi: 10.1016/j.jad.2018.06.024. Epub 2018 Jun 6. J Affect Disord. 2018. PMID: 29933216
-
Association between common stressful life events and coping strategies in adults.J Educ Health Promot. 2021 Aug 31;10:307. doi: 10.4103/jehp.jehp_519_20. eCollection 2021. J Educ Health Promot. 2021. PMID: 34667807 Free PMC article.
-
[From life events to symptoms of anxiety and depression: the role of dysfunctional attitudes and coping].Ideggyogy Sz. 2014 Nov 30;67(11-12):397-408. Ideggyogy Sz. 2014. PMID: 25720242 Hungarian.
-
[Multidimensional assessment of coping: validation of the Brief COPE among French population].Encephale. 2003 Nov-Dec;29(6):507-18. Encephale. 2003. PMID: 15029085 French.
References
-
- Ghaderi S, Sahaf R, Mohammadi Shahbalaghi F, Ansari G, Gharanjic A, Ashrafi K, et al. Prevalence of depression in elderly Kurdish community residing in Boukan, Iran. Salmand Iran J Ageing. 2012;7:57–66.
-
- Beekman AT, Geerlings SW, Deeg DJ, Smit JH, Schoevers RS, de Beurs E, et al. The natural history of late-life depression: A 6-year prospective study in the community. Arch Gen Psychiatry. 2002;59:605–11. - PubMed
-
- Roberts RE, Shema SJ, Kaplan GA, Strawbridge WJ. Sleep complaints and depression in an aging cohort: A prospective perspective. Am J Psychiatry. 2000;157:81–8. - PubMed
-
- Sajadi H, Mohaqeqi Kamal H, Vameghi M, Forozan AS, Rafei H, Nosratabadi M. Systematic review of prevalence and risk factors associated with depression and its treatment in Iranian elderly. Iran J Ageing. 2013;7:7–15.
-
- Gulseren S, Gulseren L, Hekimsoy Z, Cetinay P, Ozen C, Tokatlioglu B. Depression, anxiety, health-related quality of life, and disability in patients with overt and subclinical thyroid dysfunction. Arch Med Res. 2006;37:133–9. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials