Could Fibroblast Activation Protein (FAP)-Specific Radioligands Be Considered as Pan-Tumor Agents?
- PMID: 35280710
- PMCID: PMC8888077
- DOI: 10.1155/2022/3948873
Could Fibroblast Activation Protein (FAP)-Specific Radioligands Be Considered as Pan-Tumor Agents?
Abstract
Background: Cancer-associated fibroblasts (CAFs) can strongly modulate the response to therapy of malignant tumor cells, facilitating their continuous proliferation and invading behaviors. In this context, several efforts were made in identifying the fibroblast activation protein (FAP) as a CAF recognizer and in designing FAP-specific PET radiotracers (as 68Ga-FAPI) along with FAP-specific therapeutic radioligands. Herein, we review different clinical studies using the various FAP-specific radioligands as novel theranostic agents in a wide range of oncologic and nononcologic indications.
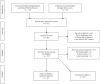
Methods: A comprehensive systematic search was conducted on the PubMed and Scopus databases to find relevant published articles concerning the FAP-specific PET imaging as well as the FAP-specific radionuclide therapy in patients with oncologic and nononcologic indications. The enrolled studies were dichotomized into oncologic and nononcologic categories, and the required data were extracted by precisely reviewing the whole text of each eligible study. A meta-analysis was also performed comparing the detection rates of 68Ga-FAPI vs. 18F-FDG PET/CT using odds ratio (OR) and risk difference as outcome measures.
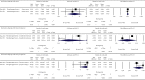
Results: Of the initial 364 relevant papers, 49 eligible articles (1479 patients) and 55 case reports were enrolled in our systematic review. These studies observed high radiolabeled FAPI avidity as early as 10 minutes after administration in primary sites of various malignant tumors. Based on the meta-analysis which was done on the reported detection rates of the 68Ga-FAPI and 18F-FDG PET/CT scans, the highest OR belonged to the primary lesion detection rate of gastrointestinal tumors (OR = 32.079, 95% CI: 4.001-257.212; p = 0.001) with low heterogeneity (I2 = 0%). The corresponding value of the nodal metastases belonged to hepatobiliary tumors (OR = 11.609, 95% CI: 1.888-71.365; p = 0.008) with low heterogeneity (I2 = 0%). For distant metastases, the highest estimated OR belonged to nasopharyngeal carcinomas (OR = 77.451, 95% CI: 7.323-819.201; p < 0.001) with low heterogeneity (I2 = 0%).
Conclusions: The outperformance of 68Ga-FAPI PET/CT over 18F-FDG PET/CT in identifying certain primary tumors as well as in detecting their metastatic lesions may open indications for evaluation of cases with inconclusive 18F-FDG PET/CT findings. What needs to be emphasized is that the false-positive results might be problematic and must be taken into account in 68Ga-FAPI PET/CT interpretation. More clarification on the role of FAPI radioligands in oncologic imaging, radionuclide therapy, and radiotherapy treatment planning is therefore required.
Copyright © 2022 Hessamoddin Roustaei et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that there are no conflicts of interest regarding the publication of this article.
Figures



References
-
- Ferlay J., Ervik M., Lam F. Global Cancer Observatory: Cancer Today . Lyon, France: International Agency for Research on Cancer, WHO Cancer Today; 2021. https://gco.iarc.fr/today/home .
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
