Differentiation Between Benign and Metastatic Breast Lymph Nodes Using Apparent Diffusion Coefficients
- PMID: 35280791
- PMCID: PMC8905522
- DOI: 10.3389/fonc.2022.795265
Differentiation Between Benign and Metastatic Breast Lymph Nodes Using Apparent Diffusion Coefficients
Abstract
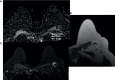
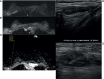
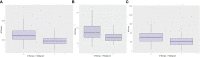
The aim of this study was to determine the range of apparent diffusion coefficient (ADC) values for benign axillary lymph nodes in contrast to malignant axillary lymph nodes, and to define the optimal ADC thresholds for three different ADC parameters (minimum, maximum, and mean ADC) in differentiating between benign and malignant lymph nodes. This retrospective study included consecutive patients who underwent breast MRI from January 2017-December 2020. Two-year follow-up breast imaging or histopathology served as the reference standard for axillary lymph node status. Area under the receiver operating characteristic curve (AUC) values for minimum, maximum, and mean ADC (min ADC, max ADC, and mean ADC) for benign vs malignant axillary lymph nodes were determined using the Wilcoxon rank sum test, and optimal ADC thresholds were determined using Youden's Index. The final study sample consisted of 217 patients (100% female, median age of 52 years (range, 22-81), 110 with benign axillary lymph nodes and 107 with malignant axillary lymph nodes. For benign axillary lymph nodes, ADC values (×10-3 mm2/s) ranged from 0.522-2.712 for mean ADC, 0.774-3.382 for max ADC, and 0.071-2.409 for min ADC; for malignant axillary lymph nodes, ADC values (×10-3 mm2/s) ranged from 0.796-1.080 for mean ADC, 1.168-1.592 for max ADC, and 0.351-0.688 for min ADC for malignant axillary lymph nodes. While there was a statistically difference in all ADC parameters (p<0.001) between benign and malignant axillary lymph nodes, boxplots illustrate overlaps in ADC values, with the least overlap occurring with mean ADC, suggesting that this is the most useful ADC parameter for differentiating between benign and malignant axillary lymph nodes. The mean ADC threshold that resulted in the highest diagnostic accuracy for differentiating between benign and malignant lymph nodes was 1.004×10-3 mm2/s, yielding an accuracy of 75%, sensitivity of 71%, specificity of 79%, positive predictive value of 77%, and negative predictive value of 74%. This mean ADC threshold is lower than the European Society of Breast Imaging (EUSOBI) mean ADC threshold of 1.300×10-3 mm2/s, therefore suggesting that the EUSOBI threshold which was recently recommended for breast tumors should not be extrapolated to evaluate the axillary lymph nodes.
Keywords: MRI; apparent diffusion coefficient; breast cancer; diffusion-weighted imaging; lymph nodes; prognostic factors.
Copyright © 2022 Fardanesh, Thakur, Sevilimedu, Horvat, Gullo, Reiner, Eskreis-Winkler, Thakur and Pinker.
Conflict of interest statement
KP received payment for activities not related to the present article including lectures and service on speakers bureaus and for travel/accommodations/meeting expenses unrelated to activities listed from the European Society of Breast Imaging (MRI educational course, annual scientific meeting), AURA Health Technologies GmbH and Siemens Healthineers. The remaining authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures


References
-
- Oliver S, Gargano J, Marin M, Wallace M, Curran K, Chamberland M, et al. . The Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices’ Interim Recommendation for Use of Moderna COVID-19 Vaccine — United States, December 2020. MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep (2021) 69:1653–1656. doi: 10.15585/mmwr.mm695152e1 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Fisher B, Bauer M, Wickerham DL, Redmond CK, Fisher ER, Cruz AB, et al. . Relation of Number of Positive Axillary Nodes to the Prognosis of Patients With Primary Breast Cancer. An NSABP Update. Cancer (1983) 52:1551–7. doi: 10.1002/1097-0142(19831101)52:9<1551::aid-cncr2820520902>3.0.co;2-3 - DOI - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

