The Potential Roles of Exosomal Non-Coding RNAs in Hepatocellular Carcinoma
- PMID: 35280805
- PMCID: PMC8912917
- DOI: 10.3389/fonc.2022.790916
The Potential Roles of Exosomal Non-Coding RNAs in Hepatocellular Carcinoma
Abstract
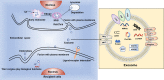
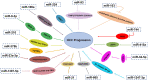
Hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) is the sixth highest-incidence cancer and the 4th most deadly cancer all over the world, with a high fatality and low diagnostic rate. Nowadays, Excessive alcohol consumption, type-2 diabetes, smoking and obesity have become some primary risk factors of HCC. As intercellular messenger transporting information cargoes between cells, exosomes are a type of extracellular vesicles (EVs) released by most types of cells including tumor cells and non-tumor cells and play a pivotal role in establishing an HCC microenvironment. Exosomes, and more generally EVs, contain different molecules, including messenger RNAs (mRNAs), non-coding RNAs (ncRNAs), proteins, lipids and transcription factors. The three main ncRNAs in exosomes are microRNAs (miRNAs), long non-coding RNAs (lncRNAs), circular RNAs (circRNAs). NcRNAs, identified as essential components, are selectively sorted into exosomes and exosomal ncRNAs show great potential in regulating tumor development, including proliferation, invasion, angiogenesis, metastasis, immune escape and drug resistance. Here, we chiefly review the formation and uptake of exosomes, classification of exosomal ncRNAs and current research on the roles of exosomal ncRNAs in HCC progression. We also explored their clinical applications as new diagnostic biomarkers and therapeutic avenues in HCC.
Keywords: diagnostic biomarkers; exosomal non-coding RNAs; exosome; extracellular vesicles; hepatocellular carcinoma; therapeutic target.
Copyright © 2022 Wang, Hao, Song, Chu and Wang.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

