Coronavirus disease 2019 and the global economy
- PMID: 35280846
- PMCID: PMC8896980
- DOI: 10.1016/j.tranpol.2022.03.003
Coronavirus disease 2019 and the global economy
Abstract
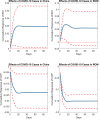
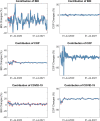
Using daily data on the coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) cases from China and the rest of the world, this paper investigates the corresponding effects on the global economic activity. The empirical results based on a structural vector autoregression model using crude oil prices (COP) and the Baltic Exchange Dry Index (BDI) are consistent with increases in COVID-19 cases acting as negative demand shocks in the global economic activity (reflected as reductions in COP) and negative supply shocks in the global transportation of commodities (reflected as increases in BDI). The historical decomposition results further suggest that the effects of COVID-19 cases on COP and BDI have been mostly observed in the early COVID-19 period.
Keywords: Baltic dry index; COVID-19; Coronavirus; Crude oil prices.
© 2022 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Figures


References
-
- Araz O.M., Choi T.-M., Olson D., Salman F.S. Decision Sciences; 2020. Data Analytics for Operational Risk Management.
-
- Baldwin R., di Mauro B.W. CEPR Press VoxEU. org; 2020. Economics in the Time of COVID-19.
-
- Baldwin R., Tomiura E. CEPR Press VoxEU. org; 2020. Thinking Ahead about the Trade Impact of COVID-19.
-
- Bildirici M.E., Kayıkçı F., Onat I.Ş. Baltic Dry Index as a major economic policy indicator: the relationship with economic growth. Proc. Soc. Behav. Sci. 2015;210:416–424.
-
- Büyüktahtakın İ.E., des Bordes E., Kıbış E.Y. A new epidemics–logistics model: insights into controlling the Ebola virus disease in West Africa. Eur. J. Oper. Res. 2018;265(3):1046–1063.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
