Memory B Cells Induced by Sputnik V Vaccination Produce SARS-CoV-2 Neutralizing Antibodies Upon Ex Vivo Restimulation
- PMID: 35280987
- PMCID: PMC8907154
- DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.840707
Memory B Cells Induced by Sputnik V Vaccination Produce SARS-CoV-2 Neutralizing Antibodies Upon Ex Vivo Restimulation
Abstract
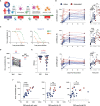
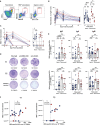
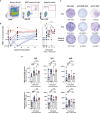
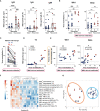
The development of effective vaccines against SARS-CoV-2 remains a global health priority. Despite extensive use, the effects of Sputnik V on B cell immunity need to be explored in detail. We performed comprehensive profiling of humoral and B cell responses in a cohort of vaccinated subjects (n = 22), and demonstrate that Sputnik vaccination results in robust B cell immunity. We show that B memory cell (MBC) and antibody responses to Sputnik V were heavily dependent on whether the vaccinee had a history of SARS-CoV-2 infection or not. 85 days after the first dose of the vaccine, ex vivo stimulated MBCs from the vast majority of Sputnik V vaccinees produced antibodies that robustly neutralized the Wuhan Spike-pseudotyped lentivirus. MBC-derived antibodies from all previously infected and some of the naïve vaccine recipients could also cross-neutralize Beta (B.1.351) variant of SARS-CoV-2. Virus-neutralizing activity of MBC-derived antibodies correlated well with that of the serum antibodies, suggesting the interplay between the MBC and long-lived plasma cell responses. Thus, our in-depth analysis of MBC responses in Sputnik V vaccinees complements traditional serological approaches and may provide important outlook into future B cell responses upon re-encounter with the emerging variants of SARS-CoV-2.
Keywords: COVID-19; SARS-CoV-2; Sputnik V vaccine; memory B cells; vaccination.
Copyright © 2022 Byazrova, Kulemzin, Astakhova, Belovezhets, Efimov, Chikaev, Kolotygin, Gorchakov, Taranin and Filatov.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Logunov DY, Dolzhikova IV, Shcheblyakov DV, Tukhvatulin AI, Zubkova OV, Dzharullaeva AS, et al. Safety and Efficacy of an Rad26 and Rad5 Vector-Based Heterologous Prime-Boost COVID-19 Vaccine: An Interim Analysis of a Randomised Controlled Phase 3 Trial in Russia. Lancet (2021) 397:671–81. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(21)00234-8 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

