Regulatory T Cells: Angels or Demons in the Pathophysiology of Sepsis?
- PMID: 35281010
- PMCID: PMC8914284
- DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.829210
Regulatory T Cells: Angels or Demons in the Pathophysiology of Sepsis?
Abstract
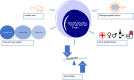
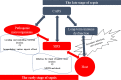
Sepsis is a syndrome characterized by life-threatening organ dysfunction caused by the dysregulated host response to an infection. Sepsis, especially septic shock and multiple organ dysfunction is a medical emergency associated with high morbidity, high mortality, and prolonged after-effects. Over the past 20 years, regulatory T cells (Tregs) have been a key topic of focus in all stages of sepsis research. Tregs play a controversial role in sepsis based on their heterogeneous characteristics, complex organ/tissue-specific patterns in the host, the multi-dimensional heterogeneous syndrome of sepsis, the different types of pathogenic microbiology, and even different types of laboratory research models and clinical research methods. In the context of sepsis, Tregs may be considered both angels and demons. We propose that the symptoms and signs of sepsis can be attenuated by regulating Tregs. This review summarizes the controversial roles and Treg checkpoints in sepsis.
Keywords: checkpoints; pathophysiology; regulatory T cells; secondary infections; sepsis.
Copyright © 2022 Gao, Yao, Zhang, Chen, Meng, Chen, Wang, Liu, Tian, Shou and Chai.
Conflict of interest statement
XT was employed by Beijing Qiansong Technology Development Company. The remaining authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
The roles of tissue-resident macrophages in sepsis-associated organ dysfunction.Heliyon. 2023 Oct 30;9(11):e21391. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2023.e21391. eCollection 2023 Nov. Heliyon. 2023. PMID: 38027963 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Removal of increased circulating CD4+CD25+Foxp3+ regulatory T cells in patients with septic shock using hemoperfusion with polymyxin B-immobilized fibers.Surgery. 2013 Feb;153(2):262-71. doi: 10.1016/j.surg.2012.06.023. Epub 2012 Aug 9. Surgery. 2013. PMID: 22884251
-
Increased Expression of Programmed Cell Death-1 in Regulatory T Cells of Patients with Severe Sepsis and Septic Shock: An Observational Clinical Study.Scand J Immunol. 2017 Nov;86(5):408-417. doi: 10.1111/sji.12612. Epub 2017 Oct 5. Scand J Immunol. 2017. PMID: 28888058
-
The role of regulatory T cells in the pathogenesis of sepsis and its clinical implication.J Interferon Cytokine Res. 2012 Aug;32(8):341-9. doi: 10.1089/jir.2011.0080. Epub 2012 Jul 16. J Interferon Cytokine Res. 2012. PMID: 22799563 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Neutralization of interleukin-10 or transforming growth factor-β decreases the percentages of CD4+ CD25+ Foxp3+ regulatory T cells in septic mice, thereby leading to an improved survival.Surgery. 2012 Feb;151(2):313-22. doi: 10.1016/j.surg.2011.07.019. Epub 2011 Oct 6. Surgery. 2012. PMID: 21982068
Cited by
-
The Application Potential of the Regulation of Tregs Function by Irisin in the Prevention and Treatment of Immune-Related Diseases.Drug Des Devel Ther. 2024 Jul 16;18:3005-3023. doi: 10.2147/DDDT.S465713. eCollection 2024. Drug Des Devel Ther. 2024. PMID: 39050796 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Influence of early enteral nutrition plus probiotics on intestinal function of senile patients with sepsis.Am J Transl Res. 2023 Jan 15;15(1):445-451. eCollection 2023. Am J Transl Res. 2023. PMID: 36777858 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of cuproptosis-related gene clusters and immune cell infiltration in major burns based on machine learning models and experimental validation.Front Immunol. 2024 Feb 12;15:1335675. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2024.1335675. eCollection 2024. Front Immunol. 2024. PMID: 38410514 Free PMC article.
-
Herbacetin ameliorates lipopolysaccharide-elicited inflammatory response by suppressing NLRP-3/AIM-2 inflammasome activation, PI3K/Akt/MAPKs/NF-κB redox inflammatory signalling, modulating autophagy and macrophage polarization imbalance.Mol Biol Rep. 2024 Nov 16;51(1):1159. doi: 10.1007/s11033-024-10068-9. Mol Biol Rep. 2024. PMID: 39549151
-
Novel therapeutic role of Ganoderma Polysaccharides in a septic mouse model - The key role of macrophages.Heliyon. 2024 Feb 20;10(5):e26732. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e26732. eCollection 2024 Mar 15. Heliyon. 2024. PMID: 38449666 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Weiss SL, Peters MJ, Alhazzani W, Agus MSD, Flori HR, Inwald DP, et al. . Surviving Sepsis Campaign International Guidelines for the Management of Septic Shock and Sepsis-Associated Organ Dysfunction in Children. Pediatr Crit Care Med (2020) 21(2):e52–106. doi: 10.1097/PCC.0000000000002198 - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

