STAT6 Blockade Abrogates Aspergillus-Induced Eosinophilic Chronic Rhinosinusitis and Asthma, A Model of Unified Airway Disease
- PMID: 35281012
- PMCID: PMC8904741
- DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.818017
STAT6 Blockade Abrogates Aspergillus-Induced Eosinophilic Chronic Rhinosinusitis and Asthma, A Model of Unified Airway Disease
Abstract
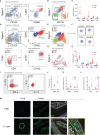
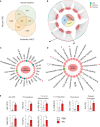
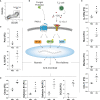
Unified airway disease, including concurrent asthma and chronic rhinosinusitis (CRS), is a common, but poorly understood disorder with no curative treatment options. To establish a murine model of chronic unified eosinophilic airway inflammation, mice were challenged with Aspergillus niger, and sinonasal mucosa and lung tissue were evaluated by immunohistochemistry, flow cytometry, and gene expression. Inhalation of A niger conidia resulted in a Th2-biased lung and sinus inflammation that typifies allergic asthma and CRS. Gene network and pathway analysis correlated with human disease with upregulation of not only the JAK-STAT and helper T-cell pathways, but also less expected pathways governing the spliceosome, osteoclast differentiation, and coagulation pathways. Utilizing a specific inhibitor and gene-deficient mice, we demonstrate that STAT6 is required for mycosis-induced sinus inflammation. These findings confirm the relevance of this new model and portend future studies that further extend our understanding of the immunopathologic basis of airway mycosis and unified airway disease.
Keywords: STAT-6; allergic; asthma; chronic rhinosinusitis; eosinophil; mouse model; mycosis; unified airway.
Copyright © 2022 Sun, Damania, Mair, Otukoya, Li, Polsky, Zeng, Alt, Citardi, Corry, Luong and Knight.
Conflict of interest statement
DC and JK hold intellectual property in PM-43I. The remaining authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest. The handling editor declared a shared affiliation with the author YZ at the time of review.
Figures




References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

