Thinned-Young Apple Polyphenols Inhibit Halitosis-Related Bacteria Through Damage to the Cell Membrane
- PMID: 35281303
- PMCID: PMC8905352
- DOI: 10.3389/fmicb.2021.745100
Thinned-Young Apple Polyphenols Inhibit Halitosis-Related Bacteria Through Damage to the Cell Membrane
Abstract
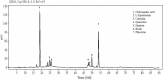
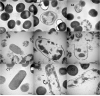
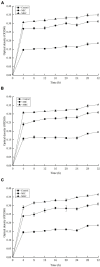
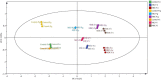
The thinned young apple is a by-product and is generally discarded in the orchard during fruit thinning. The polyphenol content of thinned young apples is about 10 times more than that of ripe apples. In our study, the antibacterial effect of thinned young apple polyphenols (YAP) on the halitosis-related bacteria including Porphyromonas gingivalis, Prevotella intermedius, and Fusobacterium nucleatum was investigated. The minimum inhibitory concentrations of YAP against P. gingivalis, P. intermedia, and F. nucleatum were 8.0, 8.0, and 12.0 mg/ml, while the minimum bactericidal concentrations were 10.0, 10.0, and 14.0 mg/ml, respectively. The scanning electron microscopy and transmission electron microscopy analyses showed that after YAP treatment, the membrane surface of halitosis-related bacterial cells was coarse and the cell wall and membrane were separated and eventually ruptured. The integrity of the cell membrane was determined by flow cytometry, indicating that the cells with the integrity membrane significantly reduced as the YAP concentration treatment increased. The release of proteins and nucleic acids into the cell suspension significantly increased, and the membrane potential reduced after the YAP treatment. This research illustrated the antibacterial mechanism of YAP against halitosis-related bacteria and provided a scientific basis of utilizing the polyphenols from the discarded thinned young apples.
Keywords: Thinned-young apple polyphenols; antibacterial mechanism; cell membrane; halitosis; membrane potential.
Copyright © 2022 Liu, Shen, Wang, Zhou, Zhao, Yang and Guo.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures




References
-
- Bajpai V. K., Sharma A., Baek K. H. (2013). Antibacterial mode of action of Cudrania tricuspidata fruit essential oil, affecting membrane permeability and surface characteristics of food-borne pathogens. Food Control 32 582–590. 10.1016/j.foodcont.2013.01.032 - DOI
-
- Ben L. A., Dudonné S., Desjardins Y., Grenier D. (2015). Wild Blueberry (Vaccinium angustifolium Ait.) Polyphenols Target Fusobacterium nucleatum and the Host Inflammatory Response: potential Innovative Molecules for Treating Periodontal Diseases. J. Agric. Food. Chem. 63 6999–7008. 10.1021/acs.jafc.5b01525 - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

