Impact of Donepezil on Brain Glucose Metabolism Assessed Using [18F]2-Fluoro-2-deoxy-D-Glucose Positron Emission Tomography Imaging in a Mouse Model of Alzheimer's Disease Induced by Intracerebroventricular Injection of Amyloid-Beta Peptide
- PMID: 35281502
- PMCID: PMC8916213
- DOI: 10.3389/fnins.2022.835577
Impact of Donepezil on Brain Glucose Metabolism Assessed Using [18F]2-Fluoro-2-deoxy-D-Glucose Positron Emission Tomography Imaging in a Mouse Model of Alzheimer's Disease Induced by Intracerebroventricular Injection of Amyloid-Beta Peptide
Abstract
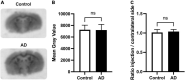
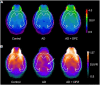
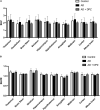
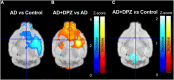
Translational methods are needed to monitor the impact of the Alzheimer's disease (AD) and therapies on brain function in animal models and patients. The formation of amyloid plaques was investigated using [18F]florbetapir autoradiography in a mouse model of AD consisting in unilateral intracerebroventricular (i.c.v) injection of amyloid peptide Aβ25-35. Then, an optimized positron emission tomography (PET) imaging protocol using [18F]2-fluoro-2-deoxy-D-glucose ([18F]FDG) was performed to estimate brain glucose metabolism: [18F]FDG was injected in awake animals to allow for 40 min brain uptake in freely moving mice. Anesthesia was then induced for 30 min PET acquisition to capture the slow and poorly reversible brain uptake of [18F]FDG. Impact of donepezil (0.25 mg/kg daily, 7 days, orally) on brain function was investigated in AD mice (n = 6 mice/group). Formation of amyloid plaques could not be detected using autoradiography. Compared with sham controls (injection of scramble peptide), significant decrease in [18F]FDG uptake was observed in the AD group in the subcortical volume of the ipsilateral hemisphere. Donepezil restored normal glucose metabolism by selectively increasing glucose metabolism in the affected subcortical volume but not in other brain regions. In mice, [18F]FDG PET imaging can be optimized to monitor impaired brain function associated with i.c.v injection of Aβ25-35, even in the absence of detectable amyloid plaque. This model recapitulates the regional decrease in [18F]FDG uptake observed in AD patients. [18F]FDG PET imaging can be straightforwardly transferred to AD patients and may aid the development of certain therapies designed to restore the altered brain function in AD.
Keywords: Alzheimer’s disease; Alzheimer’s mouse model; PET imaging; awake brain imaging; donepezil; functional imaging (positron emission tomography).
Copyright © 2022 Hugon, Goutal, Sarazin, Bottlaender, Caillé, Droguerre, Charvériat, Winkeler and Tournier.
Conflict of interest statement
MD and MC were full-time employees of Theranexus Company. The authors declare that this study received funding from Theranexus Company. The funder had the following involvement in the study: Study design, interpretation of the results. The remaining authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Auvity S., Tonietto M., Caillé F., Bodini B., Bottlaender M., Tournier N., et al. (2020). Repurposing radiotracers for myelin imaging: a study comparing 18F-florbetaben, 18F-florbetapir, 18F-flutemetamol,11C-MeDAS, and 11C-PiB. Eur. J. Nucl. Med. Mol. Imaging 47 490–501. 10.1007/s00259-019-04516-z - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

