Regulation of Cell Delamination During Cortical Neurodevelopment and Implication for Brain Disorders
- PMID: 35281509
- PMCID: PMC8904418
- DOI: 10.3389/fnins.2022.824802
Regulation of Cell Delamination During Cortical Neurodevelopment and Implication for Brain Disorders
Abstract
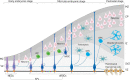
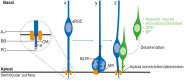
Cortical development is dependent on key processes that can influence apical progenitor cell division and progeny. Pivotal among such critical cellular processes is the intricate mechanism of cell delamination. This indispensable cell detachment process mainly entails the loss of apical anchorage, and subsequent migration of the mitotic derivatives of the highly polarized apical cortical progenitors. Such apical progenitor derivatives are responsible for the majority of cortical neurogenesis. Many factors, including transcriptional and epigenetic/chromatin regulators, are known to tightly control cell attachment and delamination tendency in the cortical neurepithelium. Activity of these molecular regulators principally coordinate morphogenetic cues to engender remodeling or disassembly of tethering cellular components and external cell adhesion molecules leading to exit of differentiating cells in the ventricular zone. Improper cell delamination is known to frequently impair progenitor cell fate commitment and neuronal migration, which can cause aberrant cortical cell number and organization known to be detrimental to the structure and function of the cerebral cortex. Indeed, some neurodevelopmental abnormalities, including Heterotopia, Schizophrenia, Hydrocephalus, Microcephaly, and Chudley-McCullough syndrome have been associated with cell attachment dysregulation in the developing mammalian cortex. This review sheds light on the concept of cell delamination, mechanistic (transcriptional and epigenetic regulation) nuances involved, and its importance for corticogenesis. Various neurodevelopmental disorders with defective (too much or too little) cell delamination as a notable etiological underpinning are also discussed.
Keywords: cell adhesion; cell polarity; cortical development; delamination; epigenetic regulation; neurepithelium; neurodevelopmental disorders; transcription factors.
Copyright © 2022 Sokpor, Brand-Saberi, Nguyen and Tuoc.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Abbas E., Hassan M. A., Sokpor G., Kiszka K., Pham L., Kerimoglu C., et al. (2021). Conditional Loss of BAF (mSWI/SNF) Scaffolding Subunits Affects Specification and Proliferation of Oligodendrocyte Precursors in Developing Mouse Forebrain. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 9:619538. 10.3389/fcell.2021.619538 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

