Comparative Proteomic Analysis Reveals Antibacterial Mechanism of Patrinia scabiosaefolia Against Methicillin Resistant Staphylococcus epidermidis
- PMID: 35281570
- PMCID: PMC8912936
- DOI: 10.2147/IDR.S350715
Comparative Proteomic Analysis Reveals Antibacterial Mechanism of Patrinia scabiosaefolia Against Methicillin Resistant Staphylococcus epidermidis
Abstract
Purpose: As a kind of opportunist pathogen, Staphylococcus epidermidis (MRSE) can cause nosocomial infections and easily evolve into resistant bacteria. Among these, methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus epidermidis (MRSE) exhibit significantly higher rates. Our previous study showed that Patrinia scabiosaefolia (PS) possessed strong antibacterial activity against MRSE. However, the mechanism of PS against MRSE is not clear.
Methods: Here, a tandem mass tag-based (TMT) proteomic analysis was performed to elucidate the potential mechanism of PS against MRSE. We compared the differential expression proteins of MRSE under PS stress.
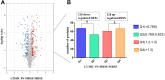
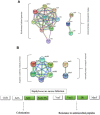
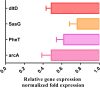
Results: Based on a fold change of >1.2 or < 1/1.2 (with p value set at <0.05), a total of 248 proteins (128 up-regulated proteins, 120 down-regulated proteins) were identified. Bioinformatic analysis showed that proteins including arginine deiminase (arcA), ornithine carbamoyltransferase (arcB) and carbamate kinase (arcC), serine-tRNA ligase (serS), phenylalanine-tRNA ligase beta and subunit (pheT), DltD (dlt), d-alanyl carrier protein (dlt), accumulation-associated protein (SasG), serine-aspartate repeat-containing protein C (SdrC) and hemin transport system permease protein HrtB (VraG) played important roles in mechanism of PS against MRSE.
Conclusion: In summary, these results indicated that arginine deiminase pathway (ADI) pathway, protein synthesis, cell wall synthesis, biofilm formation and uptake of iron were related to mechanisms of PS against MRSE. Our findings provide an insight into the the mechanism of PS against MRSE, and may be valuable in offering new targets to develop more anti-MRSE drugs.
Keywords: Patrinia scabiosaefolia; methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus epidermidis; proteomic.
© 2022 Liu et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest in this work.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Emilia sonchifolia (L.) DC. inhibits the growth of Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus epidermidis by modulating its physiology through multiple mechanisms.Sci Rep. 2025 Mar 21;15(1):9779. doi: 10.1038/s41598-025-93561-w. Sci Rep. 2025. PMID: 40119097 Free PMC article.
-
Antibacterial Mechanism of Patrinia scabiosaefolia Against Methicillin Resistant Staphylococcus epidermidis.Infect Drug Resist. 2023 Mar 10;16:1345-1355. doi: 10.2147/IDR.S398227. eCollection 2023. Infect Drug Resist. 2023. PMID: 36925724 Free PMC article.
-
Repurposing of the Tamoxifen Metabolites to Treat Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus epidermidis and Vancomycin-Resistant Enterococcus faecalis Infections.Microbiol Spectr. 2021 Oct 31;9(2):e0040321. doi: 10.1128/Spectrum.00403-21. Epub 2021 Oct 20. Microbiol Spectr. 2021. PMID: 34668743 Free PMC article.
-
Dissimilarity of ccrAB gene sequences between methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus epidermidis and methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus among bovine isolates in Korea.J Vet Sci. 2013;14(3):299-305. doi: 10.4142/jvs.2013.14.3.299. Epub 2013 Jun 30. J Vet Sci. 2013. PMID: 23820199 Free PMC article.
-
A five-year systematic review and meta-analysis study on methicillin resistant Staphylococcus epidermidis strains in Iran.Iran J Microbiol. 2023 Feb;15(1):10-18. doi: 10.18502/ijm.v15i1.11913. Iran J Microbiol. 2023. PMID: 37069903 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Study on Antibacterial Activity and Mechanism of Improved Dian Dao San Against Cutibacterium acnes (C. acnes).Infect Drug Resist. 2023 Aug 1;16:4965-4975. doi: 10.2147/IDR.S419161. eCollection 2023. Infect Drug Resist. 2023. PMID: 37546368 Free PMC article.
-
Emilia sonchifolia (L.) DC. inhibits the growth of Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus epidermidis by modulating its physiology through multiple mechanisms.Sci Rep. 2025 Mar 21;15(1):9779. doi: 10.1038/s41598-025-93561-w. Sci Rep. 2025. PMID: 40119097 Free PMC article.
-
Antibacterial Mechanism of Patrinia scabiosaefolia Against Methicillin Resistant Staphylococcus epidermidis.Infect Drug Resist. 2023 Mar 10;16:1345-1355. doi: 10.2147/IDR.S398227. eCollection 2023. Infect Drug Resist. 2023. PMID: 36925724 Free PMC article.
-
A synthetic antibiotic class with a deeply-optimized design for overcoming bacterial resistance.Nat Commun. 2024 Jul 18;15(1):6040. doi: 10.1038/s41467-024-50453-3. Nat Commun. 2024. PMID: 39019927 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Al-Awadi AQ, Ahmed M. Antimicrobial activity of chamomile extract against multidrug resistance Pseudomonas aeruginosa and Staphylococcus epidermidis during experimental skin infections in mice. In: (EurasianSciEnTech 2018) November 22-23, 2018/Ankara, Turkey: 2019; 2019.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

