Biosynthesis of Secondary Metabolites Based on the Regulation of MicroRNAs
- PMID: 35281611
- PMCID: PMC8916866
- DOI: 10.1155/2022/9349897
Biosynthesis of Secondary Metabolites Based on the Regulation of MicroRNAs
Abstract
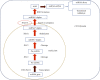
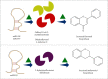
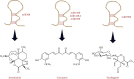
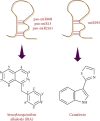
MicroRNA (miRNA), a noncoding ribonucleic acid, is considered to be important for the progression of gene expression in plants and animals by rupture or translational repression of targeted mRNAs. Many types of miRNA regulate plant metabolism, growth, and response to biotic and abiotic factors. miRNA characterization helps to expose its function in regulating the process of post-transcriptional genetic regulation. There are a lot of factors associated with miRNA function, but the function of miRNA in the organic synthesis of by-products by natural products is not yet fully elucidated. The current review is aimed at observing and characterizing miRNAs and identifying those involved in the functioning of the biosynthesis of secondary metabolites in plants, with their use in controlled manipulation.
Copyright © 2022 Rajib Hossain et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declared no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
MicroRNAs and their regulatory roles in animals and plants.J Cell Physiol. 2007 Feb;210(2):279-89. doi: 10.1002/jcp.20869. J Cell Physiol. 2007. PMID: 17096367 Review.
-
Noncoding RNAs in regulation of plant secondary metabolism.Plant Physiol Biochem. 2024 Jun;211:108718. doi: 10.1016/j.plaphy.2024.108718. Epub 2024 May 9. Plant Physiol Biochem. 2024. PMID: 38733939 Review.
-
[The role of miR319 in plant development regulation].Yi Chuan. 2011 Nov;33(11):1203-11. doi: 10.3724/sp.j.1005.2011.01203. Yi Chuan. 2011. PMID: 22120075 Review. Chinese.
-
microRNA biogenesis, degradation and activity in plants.Cell Mol Life Sci. 2015 Jan;72(1):87-99. doi: 10.1007/s00018-014-1728-7. Epub 2014 Sep 11. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2015. PMID: 25209320 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Fine-tuning plant valuable secondary metabolite biosynthesis via small RNA manipulation: strategies and potential.Planta. 2024 Sep 10;260(4):89. doi: 10.1007/s00425-024-04521-z. Planta. 2024. PMID: 39254898 Review.
Cited by
-
Exploring pharmacological potential of Aegle marmelos: integrating traditional knowledge with modern physiology and molecular biology.Physiol Mol Biol Plants. 2025 Apr;31(4):521-543. doi: 10.1007/s12298-025-01586-2. Epub 2025 May 22. Physiol Mol Biol Plants. 2025. PMID: 40443470 Review.
-
Cucurbitacins as potential anticancer agents: new insights on molecular mechanisms.J Transl Med. 2022 Dec 31;20(1):630. doi: 10.1186/s12967-022-03828-3. J Transl Med. 2022. PMID: 36585670 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Bidirectional Interplay Among Non-Coding RNAs, the Microbiome, and the Host During Development and Diseases.Genes (Basel). 2025 Feb 8;16(2):208. doi: 10.3390/genes16020208. Genes (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40004537 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Genomic and cell-specific regulation of benzylisoquinoline alkaloid biosynthesis in opium poppy.J Exp Bot. 2025 Jan 1;76(1):35-51. doi: 10.1093/jxb/erae317. J Exp Bot. 2025. PMID: 39046316 Free PMC article. Review.
-
RNA signaling in medicinal plants: An overlooked mechanism for phytochemical regulation.Biochem Biophys Rep. 2025 Apr 29;42:102032. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrep.2025.102032. eCollection 2025 Jun. Biochem Biophys Rep. 2025. PMID: 40342531 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

