Radial Endobronchial Ultrasound for Lung Cancer Diagnosis: Tips and Tricks
- PMID: 35281877
- PMCID: PMC8899369
- DOI: 10.7150/jca.67113
Radial Endobronchial Ultrasound for Lung Cancer Diagnosis: Tips and Tricks
Abstract
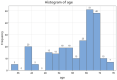
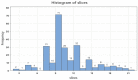
Introduction: Endoscopic techniques have been upgraded in the recent 10 years. We can use the radial endobronchial ultrasound to reach distal nodules in the periphery of the lungs, but also we can use it in order to make biopsies in lesions without endobronchial findings. Patients and Methods: We included in our study 248 patients with pulmonary nodules up to 4 cm. We use a radial endobronchial system from FUJI, a PENTAX bronchoscope and a C-ARM. We recorded the cancer type, biopsy method, time of each procedure, cell blocks and slices from cell blocks. Results: Two thirds of patients belonged to males (61.7%), forceps was the main tissue extraction technique (118, 47.6%) and tumors sized 1 to 2 cm were the most encountered (96, 38.7%). Samples with tissue content were present in 175 patients (70.6%) and one cell block dominated in the samples (109, 43.9%). Less than 20 minutes were needed to complete the operative procedure for the half patients (127, 51.2%), the C-Arm implementation concerned 117 persons (47.2%) and the majority of tumors was located in the central area of the lungs (178, 71.8%). Less time was necessary for central lesions and larger biopsy samples were acquired without the extensive use of C-ARM. Conclusion: The larger the nodule ≥2cm and in periphery the less we use the C-ARM and the time of the procedure is between 20-40 minutes. Moreover; we have more tissue sample and cell block slices.
Keywords: 22G needle; C-Arm; brush; elastography; forceps; lung cancer; metastasis; nsclc; radial ebus; sclc.
© The author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Competing Interests: The authors have declared that no competing interest exists.
Figures
References
-
- Gu Y, Chi J, Liu J, Yang L, Zhang B, Yu D. et al. A survey of computer-aided diagnosis of lung nodules from CT scans using deep learning. Computers in biology and medicine. 2021;137:104806. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

