Prognostic Value of N-Terminal Pro-B-Type Natriuretic Peptide and High-Sensitivity C-Reactive Protein in Patients With Previous Myocardial Infarction
- PMID: 35282356
- PMCID: PMC8907519
- DOI: 10.3389/fcvm.2022.797297
Prognostic Value of N-Terminal Pro-B-Type Natriuretic Peptide and High-Sensitivity C-Reactive Protein in Patients With Previous Myocardial Infarction
Abstract
Background: Patients with previous myocardial infarction (MI) have a poor prognosis and stratification for recurrent major adverse cardiovascular events (MACE) among these patients is of considerable interest. N-terminal pro-B-type natriuretic peptide (NT-proBNP) and high-sensitivity C-reactive protein (hs-CRP) are considered to be potential cardiovascular risk factors, but less is known about their prognostic importance in post-MI patients. This study aimed to evaluate the prognostic value of NT-proBNP and hs-CRP alone or together in patients who reported a prior MI.
Methods: In this prospective study, we consecutively enrolled 3,306 post-MI patients to assess the recurrent MACE. The predictive values of NT-proBNP and hs-CRP alone and together were assessed by multivariable Cox regression using hazard ratios (HR) and 95% confidence intervals (CI).
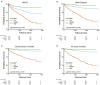
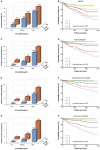
Results: During the 4-year follow-up period, 335 patients developed recurrent MACE. Multivariate Cox regression analysis showed a significant correlation between NT-proBNP levels and MACE (HR: 2.99, 95%CI: 2.06-4.36, p < 0.001), hard endpoints (HR: 5.44, 95%CI: 2.99-9.90, p < 0.001), cardiac mortality (HR: 5.92, 95%CI: 2.34-14.96, p < 0.001) and all-cause mortality (HR: 5.03, 95%CI: 2.51-10.09, p < 0.001). However, hs-CRP was not an independent predictor after adjusting for NT-proBNP. When patients were divided into six groups by using tertiles values of NT-proBNP and median values of hsCRP, patients with high NT-proBNP/hs-CRP values were 3.27 times more likely to experience MACE than patients with low NT-proBNP/hs-CRP values. The addition of NT-proBNP and hs-CRP to a prognostic model revealed a significant improvement in C-statistic, net reclassification, and integrated discrimination.
Conclusions: Increased NT-proBNP levels were associated with long-term worse outcomes and the combination of NT-proBNP and hs-CRP has an incremental value in the further risk stratification of post-MI patients.
Keywords: NT-proBNP; cardiovascular events; hs-CRP; myocardial infarction; prognosis.
Copyright © 2022 Cao, Li, Liu, Zhang, Guo, Wu, Zhu, Dong, Sun, Dou and Li.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Amino-terminal pro-B-type natriuretic peptide and high-sensitivity C-reactive protein but not cystatin C predict cardiovascular events in male patients with peripheral artery disease independently of ambulatory pulse pressure.Am J Hypertens. 2014 Mar;27(3):363-71. doi: 10.1093/ajh/hpt278. Epub 2014 Jan 27. Am J Hypertens. 2014. PMID: 24470529
-
High-sensitivity C-reactive protein and N-terminal pro-B-type natriuretic peptide in patients with stable coronary artery disease: a prognostic study within the CLARICOR trial.Scand J Clin Lab Invest. 2011 Feb;71(1):52-62. doi: 10.3109/00365513.2010.538081. Epub 2010 Nov 25. Scand J Clin Lab Invest. 2011. PMID: 21108561 Clinical Trial.
-
Prognostic Significance of Preprocedural N-Terminal Pro-B-Type Natriuretic Peptide Assessment in Diabetic Patients With Multivessel Coronary Disease Undergoing Revascularization.Front Cardiovasc Med. 2021 Oct 6;8:721260. doi: 10.3389/fcvm.2021.721260. eCollection 2021. Front Cardiovasc Med. 2021. PMID: 34692781 Free PMC article.
-
Prognostic value of brain natriuretic peptide in noncardiac surgery: a meta-analysis.Anesthesiology. 2009 Aug;111(2):311-9. doi: 10.1097/ALN.0b013e3181aaeb11. Anesthesiology. 2009. PMID: 19602961 Review.
-
Association of N-terminal pro-brain natriuretic peptide level with adverse outcomes in patients with acute myocardial infarction: A meta-analysis.Heart Lung. 2021 Nov-Dec;50(6):863-869. doi: 10.1016/j.hrtlng.2021.07.007. Epub 2021 Jul 30. Heart Lung. 2021. PMID: 34340134 Review.
Cited by
-
Loss-of-function N178T variant of the human P2Y4 receptor is associated with decreased severity of coronary artery disease and improved glucose homeostasis.Front Pharmacol. 2022 Dec 2;13:1049696. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2022.1049696. eCollection 2022. Front Pharmacol. 2022. PMID: 36532779 Free PMC article.
-
Biomarkers of Importance in Monitoring Heart Condition After Acute Myocardial Infarction.J Clin Med. 2024 Dec 29;14(1):129. doi: 10.3390/jcm14010129. J Clin Med. 2024. PMID: 39797212 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Innovations in heart failure management: The role of cutting-edge biomarkers and multi-omics integration.J Mol Cell Cardiol Plus. 2025 Mar 1;11:100290. doi: 10.1016/j.jmccpl.2025.100290. eCollection 2025 Mar. J Mol Cell Cardiol Plus. 2025. PMID: 40129519 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- An J, Zhang Y, Muntner P, Moran AE, Hsu JW, Reynolds K. Recurrent atherosclerotic cardiovascular event rates differ among patients meeting the very high risk definition according to age, sex, race/ethnicity, and socioeconomic status. J Am Heart Assoc. (2020) 9:e017310. 10.1161/JAHA.120.017310 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Li KP, Zhang HY, Xu XD, Ming Y, Li TJ, Song ST. Recombinant human brain natriuretic peptide attenuates myocardial ischemia-reperfusion injury by inhibiting CD4(+) T cell proliferation via PI3K/AKT/mTOR pathway activation. Cardiovasc Ther. (2020) 2020:1389312. 10.1155/2020/1389312 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

