miR-221/222 as biomarkers and targets for therapeutic intervention on cancer and other diseases: A systematic review
- PMID: 35282417
- PMCID: PMC8891816
- DOI: 10.1016/j.omtn.2022.02.005
miR-221/222 as biomarkers and targets for therapeutic intervention on cancer and other diseases: A systematic review
Abstract
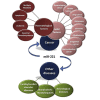
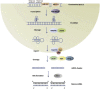
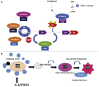
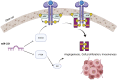
Among deregulated microRNAs (miRs) in human malignancies, miR-221 has been widely investigated for its oncogenic role and as a promising biomarker. Moreover, recent evidence suggests miR-221 as a fine-tuner of chronic liver injury and inflammation-related events. Available information also supports the potential of miR-221 silencing as promising therapeutic intervention. In this systematic review, we selected papers from the principal databases (PubMed, MedLine, Medscape, ASCO, ESMO) between January 2012 and December 2020, using the keywords "miR-221" and the specific keywords related to the most important hematologic and solid malignancies, and some non-malignant diseases, to define and characterize deregulated miR-221 as a valuable therapeutic target in the modern vision of molecular medicine. We found a major role of miR-221 in this view.
Keywords: NASH; biliary tract cancer; bladder cancer; breast cancer; cancer; cervical cancer; demyelinating diseases; endometrial cancer; gastrointestinal cancer; glioblastoma; gynecological cancers; hematological diseases; hepatocellular carcinoma; lung cancer; melanoma; miR; miR therapeutics; miR-221; miR-221/222; miRs; microRNA; myeloma; neuropathy; ovarian cancer; pancreatic cancer; pharmacokinetics; prostate cancer; renal cell carcinoma; sarcomas; solid cancers; urogenital cancer.
© 2022 The Authors.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures





References
-
- Drusco A., Croce C.M. MicroRNAs and cancer: a long story for short RNAs. Adv. Cancer Res. 2017;135:1–24. - PubMed
-
- Abba M.L., Patil N., Leupold J.H., Moniuszko M., Utikal J., Niklinski J., Allgayer H. MicroRNAs as novel targets and tools in cancer therapy. Cancer Lett. 2017;387:84–94. - PubMed
-
- Seto A.G., Beatty X., Lynch J.M., Hermreck M., Tetzlaff M., Duvic M., Jackson A.L. Cobomarsen, an oligonucleotide inhibitor of miR-155, co-ordinately regulates multiple survival pathways to reduce cellular proliferation and survival in cutaneous T-cell lymphoma. Br. J. Haematol. 2018;183:428–444. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

