Narrative review of portal vein thrombosis in cirrhosis: pathophysiology, diagnosis, and management from an interventional radiology perspective
- PMID: 35282661
- PMCID: PMC8898691
- DOI: 10.21037/cdt-21-98
Narrative review of portal vein thrombosis in cirrhosis: pathophysiology, diagnosis, and management from an interventional radiology perspective
Abstract
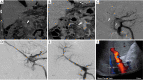
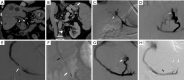
Objective: This paper examines the incidence, clinical presentation, and pathophysiology of portal vein thrombosis (PVT) in cirrhosis. Additionally, we have reviewed the literature regarding the current status of medical and interventional radiology management of PVT and have proposed a novel algorithm for the management given different clinical scenarios. Lastly two representative cases displaying endovascular treatment options are provided.
Background: Portal vein thrombus in the setting of cirrhosis is an increasingly recognized clinical issue with debate on its pathophysiology, natural course, and optimal treatment. Approximately one-third of patients are asymptomatic, and detection of the thrombus is an incidental finding on imaging performed for other reasons. In 30% to 50% of patients, PVT resolves spontaneously. However, there is increased post-transplant mortality in patients with completely occlusive PVT, therefore effective early revascularization strategies are needed for patients with complete PVT who are expected to undergo liver transplant. Additionally, no consensus has been reached regarding PVT treatment in terms of timing and type of interventions as well as type and duration of anticoagulation.
Methods: Computerized literature search as well as discussion with experts in the field.
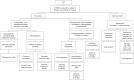
Conclusions: Management of PVT is complex, as many variables affect which treatments can be used. Anticoagulation appears to be the optimal first-line treatment in patients with acute PVT but without bleeding varices or mesenteric ischemia. Minimally invasive treatments include various methods of mechanical thrombectomy, chemical thrombolysis, and transjugular intrahepatic portosystemic shunt (TIPS) placement with or without variceal embolization. Definitive recommendations are difficult due to lack of high quality data and continued research is needed to evaluate the efficacy of different anticoagulants as well as the timing and use of various minimally invasive therapies in specific circumstances.
Keywords: Cirrhosis; intervention; narrative review; portal vein thrombosis (PVT).
2022 Cardiovascular Diagnosis and Therapy. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflicts of Interest: All authors have completed the ICMJE uniform disclosure form (available at https://cdt.amegroups.com/article/view/10.21037/cdt-21-98/coif). SP serves as an unpaid editorial board member of Cardiovascular Diagnosis and Therapy from September 2021 to August 2023. The other authors have no conflicts of interest to declare.
Figures
Similar articles
-
AGA Clinical Practice Update on Management of Portal Vein Thrombosis in Patients With Cirrhosis: Expert Review.Gastroenterology. 2025 Feb;168(2):396-404.e1. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2024.10.038. Epub 2024 Dec 20. Gastroenterology. 2025. PMID: 39708000 Review.
-
Applications of percutaneous mechanical thrombectomy in transjugular intrahepatic portosystemic shunt and portal vein thrombosis.Tech Vasc Interv Radiol. 2003 Mar;6(1):59-69. doi: 10.1053/tvir.2003.36433. Tech Vasc Interv Radiol. 2003. PMID: 12772131 Review.
-
Portal Vein Thrombosis In Cirrhosis: Interventional Treatment Options.Curr Gastroenterol Rep. 2021 Oct 15;23(12):24. doi: 10.1007/s11894-021-00826-1. Curr Gastroenterol Rep. 2021. PMID: 34654971 Review.
-
Portal vein thrombosis after partial splenic embolization in liver cirrhosis: efficacy of anticoagulation and long-term follow-up.J Vasc Interv Radiol. 2013 Dec;24(12):1808-16. doi: 10.1016/j.jvir.2013.08.018. Epub 2013 Oct 4. J Vasc Interv Radiol. 2013. PMID: 24099787
-
Nontumoral Portal Vein Thrombosis: A Challenging Consequence of Liver Cirrhosis.J Clin Transl Hepatol. 2020 Dec 28;8(4):432-444. doi: 10.14218/JCTH.2020.00067. Epub 2020 Nov 11. J Clin Transl Hepatol. 2020. PMID: 33447527 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
The Role of Contrast-Enhanced Ultrasound (CEUS) in the Detection of Neoplastic Portal Vein Thrombosis in Patients with Hepatocellular Carcinoma.Tomography. 2023 Oct 20;9(5):1976-1986. doi: 10.3390/tomography9050154. Tomography. 2023. PMID: 37888746 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Direct oral anticoagulants for the treatment of splanchnic vein thrombosis: A state of art.World J Gastroenterol. 2023 Sep 7;29(33):4962-4974. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v29.i33.4962. World J Gastroenterol. 2023. PMID: 37731994 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Classification and Management of Portal Vein Thrombosis in Cirrhotic Patients: A Narrative Review.Cureus. 2024 Jul 31;16(7):e65869. doi: 10.7759/cureus.65869. eCollection 2024 Jul. Cureus. 2024. PMID: 39219865 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Role of Imaging in Portal Vein Thrombosis: From the Diagnosis to the Interventional Radiological Management.Diagnostics (Basel). 2022 Oct 30;12(11):2628. doi: 10.3390/diagnostics12112628. Diagnostics (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36359472 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
