Sex Differences in Thrombosis and Mortality in Patients Hospitalized for COVID-19
- PMID: 35282877
- PMCID: PMC8908016
- DOI: 10.1016/j.amjcard.2022.01.024
Sex Differences in Thrombosis and Mortality in Patients Hospitalized for COVID-19
Abstract
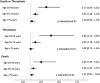
Gender-specific differences in thrombosis have been reported in hospitalized patients with COVID-19. We sought to investigate the influence of age on the relation between gender and incident thrombosis or death in COVID-19. We identified consecutive adults aged ≥18 years hospitalized with COVID-19 from March 1, 2020, to April 17, 2020, at a large New York health system. In-hospital thrombosis and all-cause mortality were evaluated by gender and stratified by age group. Logistic regression models were generated to estimate the odds of thrombosis or death after multivariable adjustment. In 3,334 patients hospitalized with COVID-19, 61% were men. Death or thrombosis occurred in 34% of hospitalizations and was more common in men (36% vs 29% in women, p <0.001; adjusted odds ratio [aOR] 1.61, 95% confidence interval [CI] 1.36 to 1.91). When stratified by age, men had a higher incidence of death or thrombosis in younger patients (aged 18 to 54 years: 21% vs 9%, aOR 3.17, 95% CI 2.06 to 5.01; aged 55 to 74 years: 39% vs 28%, aOR 1.63, 95% CI 1.28 to 2.10), but not older patients (aged ≥75 years: 55% vs 48%; aOR 1.20, 95% CI 0.90 to 1.59) (interaction p value: 0.01). For the individual end points, men were at higher risk of thrombosis (19% vs 12%; aOR 1.65, 95% CI 1.33 to 2.05) and mortality (26% vs 23%; aOR 1.41, 95% CI 1.17 to 1.69) than women, and gender-specific differences were attenuated with older age. Associations between thrombosis and mortality were most striking in younger patients (aged 18 to 54 years, aOR 8.25; aged 55 to 74 years, aOR 2.38; aged >75 years, aOR 1.88; p for interaction <0.001) but did not differ by gender. In conclusion, the risk of thrombosis or death in COVID-19 is higher in men compared with women and is most apparent in younger age groups.
Copyright © 2022. Published by Elsevier Inc.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of Competing Interest The authors have no conflicts of interest to declare.
Figures
References
-
- Bikdeli B, Madhavan MV, Jimenez D, Chuich T, Dreyfus I, Driggin E, Nigoghossian CD, Ageno W, Madjid M, Guo Y, Tang LV, Hu Y, Giri J, Cushman M, Quéré I, Dimakakos EP, Gibson CM, Lippi G, Favaloro EJ, Fareed J, Caprini JA, Tafur AJ, Burton JR, Francese DP, Wang EY, Falanga A, McLintock C, Hunt BJ, Spyropoulos AC, Barnes GD, Eikelboom JW, Weinberg I, Schulman S, Carrier M, Piazza G, Beckman JA, Steg PG, Stone GW, Rosenkranz S, Goldhaber SZ, Parikh SA, Monreal M, Krumholz HM, Konstantinides SV, Weitz JI, Lip GYH. Global COVID-19 Thrombosis Collaborative Group, Endorsed by the ISTH, NATF, ESVM, and the IUA, Supported by the ESC Working Group on Pulmonary Circulation and Right Ventricular Function. COVID-19 and thrombotic or thromboembolic disease: implications for prevention, antithrombotic therapy, and follow-up: JACC State-of-the-Art Review. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2020;75(23):2950–2973. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous