Clinical Characteristics of Patients with Chronic Urticaria and Adherence to Management Guidelines by Postgraduate Students in Dermatology: A Retrospective Single Center Study
- PMID: 35283531
- PMCID: PMC8906287
- DOI: 10.4103/ijd.ijd_446_21
Clinical Characteristics of Patients with Chronic Urticaria and Adherence to Management Guidelines by Postgraduate Students in Dermatology: A Retrospective Single Center Study
Abstract
Background: Chronic urticaria is a heterogenous skin disorder representing one of the important reasons for consultation with a dermatologist. Dermatology post-graduate students play an importanrt role in the treatment of patients with chronic urticaria.
Objective: The objective of the study was to describe clinical characteristics of patients with chronic urticaria and assess adherence to the guidelines by postgraduate students in the department of dermatology of a tertiary care center.
Materials and methods: In this retrospective study, prescriptions of patients with chronic urticaria and/or angioedema presenting to the outpatient department for 5 months were analyzed. Percentage of prescriptions adhering to international urticaria management guidelines was calculated. Urticaria Activity Score, percentage of patients receiving second-generation antihistamines, first-generation antihistamines, and other drugs was recorded. Comorbidities in patients with chronic urticaria were also noted.
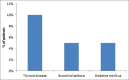
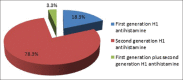
Results: A total of 60 patients (mean age 32.1 years; 58.3% male) were included in. Mean (SD) duration of urticaria at the time of study was 4.7 (2.7) months. Demographism and history of allergy to drugs was present in 45 (75%) and 4 (6.7%) patients. Mean (SD) Urticaria Activity Score was 12.5 (6.5). A total of 12 (20%) patients had comorbidities. Mean number of drugs received per patient was 1.7 (0.5). A total of 47 (78.3%) patients received second-generation antihistamines, whereas 11 (18.3%) received first-generation antihistamines. Two (3.3%) patients received combination of first-generation and second-generation antihistamines. Fexofenadine, levocetirizine, bilastine, and cetirizine was prescribed to 24 (40%), 26 (43.3%), 18 (30%), and 14 (23.3%) patients. There was no significant difference in male and female patients receiving fexofenadine (P = 0.59) or levocetirizine (P = 0.13).
Conclusion: Adherence to urticaria management guidelines by resident doctors in dermatology department in our institute was satisfactory.
Keywords: Antihistamine; first-line therapy; steroids; urticaria guideline.
Copyright: © 2022 Indian Journal of Dermatology.
Conflict of interest statement
There are no conflicts of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Chu C-Y, Al Hammadi A, Agmon-Levin N, Atakan N, Farag A, Arnaout RK, et al. Clinical characteristics and management of chronic spontaneous urticaria in patients refractory to H1-Antihistamines in Asia, Middle-East and Africa: Results from the AWARE-AMAC study. World Allergy Organ J. 2020;13:100117. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Zuberbier T, Asero R, Jensen CB, Canonica GW, Church MK, Gimnez-Arnau AM, et al. EAACI/GA2 LEN/EDF/WAO guideline: Management of urticaria. Allergy. 2009;64:1427–43. - PubMed
-
- Zuberbier T, Aberer W, Asero R, Abdul Latiff AH, Baker D, Ballmer-Weber B, et al. The EAACI/GA2LEN/EDF/WAO guideline for the definition, classification, diagnosis and management of urticaria. Allergy. 2018;73:1393–414. - PubMed
-
- Conlon NP, Edgar JDM. Adherence to best practice guidelines in Chronic spontaneous urticaria (CSU) improves patient outcome. Eur J Dermatol. 2014;24:28506. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources