Splice Junction Identification using Long Short-Term Memory Neural Networks
- PMID: 35283668
- PMCID: PMC8844938
- DOI: 10.2174/1389202922666211011143008
Splice Junction Identification using Long Short-Term Memory Neural Networks
Abstract
Background: Splice junctions are the key to move from pre-messenger RNA to mature messenger RNA in many multi-exon genes due to alternative splicing. Since the percentage of multi-exon genes that undergo alternative splicing is very high, identifying splice junctions is an attractive research topic with important implications.
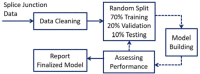
Objective: The aim of this paper is to develop a deep learning model capable of identifying splice junctions in RNA sequences using 13,666 unique sequences of primate RNA.
Methods: A Long Short-Term Memory (LSTM) Neural Network model is developed that classifies a given sequence as EI (Exon-Intron splice), IE (Intron-Exon splice), or N (No splice). The model is trained with groups of trinucleotides and its performance is tested using validation and test data to prevent bias.
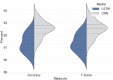
Results: Model performance was measured using accuracy and f-score in test data. The finalized model achieved an average accuracy of 91.34% with an average f-score of 91.36% over 50 runs.
Conclusion: Comparisons show a highly competitive model to recent Convolutional Neural Network structures. The proposed LSTM model achieves the highest accuracy and f-score among published alternative LSTM structures.
Keywords: LSTM; RNA-seq; Splice junction; classification; deep learning; neural networks.
© 2021 Bentham Science Publishers.
Figures


References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
