Inhibition of miR-128 Enhances Vocal Sequence Organization in Juvenile Songbirds
- PMID: 35283744
- PMCID: PMC8914539
- DOI: 10.3389/fnbeh.2022.833383
Inhibition of miR-128 Enhances Vocal Sequence Organization in Juvenile Songbirds
Abstract
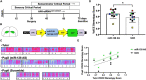
The molecular mechanisms underlying learned vocal communication are not well characterized. This is a major barrier for developing treatments for conditions affecting social communication, such as autism spectrum disorder (ASD). Our group previously generated an activity-dependent gene expression network in the striatopallidal song control nucleus, Area X, in adult zebra finches to identify master regulators of learned vocal behavior. This dataset revealed that the two host genes for microRNA-128, ARPP21 and R3HDM1, are among the top genes whose expression correlates to how much birds sing. Here we examined whether miR-128 itself is behaviorally regulated in Area X and found that its levels decline with singing. We hypothesized that reducing miR-128 during the critical period for vocal plasticity would enhance vocal learning. To test this, we bilaterally injected an antisense miR-128 construct (AS miR-128) or a control scrambled sequence into Area X at post-hatch day 30 (30 d) using sibling-matched experimental and control pupils. The juveniles were then returned to their home cage and raised with their tutors. Strikingly, inhibition of miR-128 in young birds enhanced the organization of learned vocal sequences. Tutor and pupil stereotypy scores were positively correlated, though the correlation was stronger between tutors and control pupils compared to tutors and AS miR-128 pupils. This difference was driven by AS miR-128 pupils achieving higher stereotypy scores despite their tutors' lower syntax scores. AS miR-128 birds with tutors on the higher end of the stereotypy spectrum were more likely to produce songs with faster tempos relative to sibling controls. Our results suggest that low levels of miR-128 facilitate vocal sequence stereotypy. By analogy, reducing miR-128 could enhance the capacity to learn to speak in patients with non-verbal ASD. To our knowledge, this study is the first to directly link miR-128 to learned vocal communication and provides support for miR-128 as a potential therapeutic target for ASD.
Keywords: learning; memory; microRNA; neurodevelopment; songbird; stereotypy.
Copyright © 2022 Aamodt and White.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures


References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

