Participation in One Health Networks and Involvement in the COVID-19 Pandemic Response: A Global Study
- PMID: 35284359
- PMCID: PMC8907588
- DOI: 10.3389/fpubh.2022.830893
Participation in One Health Networks and Involvement in the COVID-19 Pandemic Response: A Global Study
Abstract
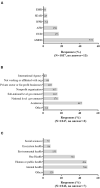
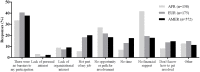
The COVID-19 pandemic exemplifies a One Health issue at the intersection of human, animal, and environmental health that requires collaboration across sectors to manage it successfully. The global One Health community includes professionals working in many different fields including human medicine, veterinary medicine, public health, ecosystem health, and, increasingly, social sciences. The aims of this cross-sectional study were to describe the involvement of the global One Health community in COVID-19 pandemic response activities. One Health networks (OHNs) have formed globally to serve professionals with common interests in collaborative approaches. We assessed the potential association between being part of an OHN and involvement in COVID-19 response activities. Data were collected in July-August 2020 using an online questionnaire that addressed work characteristics, perceived connection to OHNs, involvement in COVID-19 pandemic response activities, and barriers and facilitators to the involvement. The sample included 1,050 respondents from 94 countries across a range of organizations and work sectors including, but not restricted to, those typically associated with a One Health approach. Sixty-four percent of survey respondents indicated involvement in pandemic response activities. Being part of an OHN was positively associated with being involved in the COVID-19 response (odds ratio: 1.8, 95% confidence interval: 1.3-2.4). Lack of opportunities was a commonly reported barrier to involvement globally, with lack of funding the largest barrier in the WHO African region. This insight into diverse workforce involvement in the pandemic helps fill a gap in the global health workforce and public health education literature. An expanded understanding of the perceived roles and value of OHNs can inform targeted interventions to improve public health education and workforce capacity to prepare for and respond to public health emergencies.
Keywords: One Health; SARS-CoV-2; capacity-building; multisectoral; network; pandemic response.
Copyright © 2022 Streichert, Sepe, Jokelainen, Stroud, Berezowski and Del Rio Vilas.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- United Nations Environment Programme . Joint Tripartite and UNEP Statement on Definition of One Health. (2021). Available online at: https://wedocs.unep.org/bitstream/handle/20.500.11822/37600/JTFOWU.pdf (accessed January 9, 2022).
-
- World Health Organization . WHO-Convened Global Study of Origins of SARS-CoV-2: China Part. (Joint WHO-China Study Joint Report 14 January-10 February 2021 (2021). Available online at: https://www.who.int/health-topics/coronavirus/origins-of-the-virus (accessed April 1, 2021).
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous