Osseointegration Effect of Micro-Nano Implants Loaded With Kaempferol in Osteoporotic Rats
- PMID: 35284417
- PMCID: PMC8905647
- DOI: 10.3389/fbioe.2022.842014
Osseointegration Effect of Micro-Nano Implants Loaded With Kaempferol in Osteoporotic Rats
Abstract
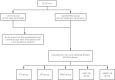
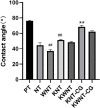
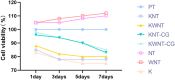
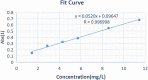
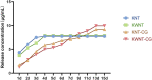
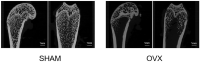
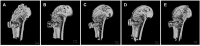
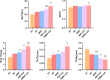
Objective: To investigate the effect of osseointegration of kaempferol loaded on the surface of micro-nanomorphic implants in ovariectomized rats. Methods: Titanium flakes were polished to obtain the PT group, anodized and acid-etched to obtain the NT and WNT groups, loaded with kaempferol to obtain the KNT and KWNT groups, and spin-coated on chitosan-gelatin composite film to obtain the KNT-CG and KWNT-CG groups. In vitro experiments were performed to observe the physicochemical properties of the titanium tablets in each group through scanning electron microscopy and contact angle experiments. The cytotoxicity and drug release pattern were observed using CCK-8 and drug release assays. An osteoporosis rat model was established. Pure titanium implants were divided into PT, NT, WNT, KNT-CG, and KWNT-CG groups after the same treatment and used in the in vivo experiments and then implanted in the femur of mice in each group. After 4 weeks, all samples were collected for toluidine blue staining, micro-computed tomography scanning, and bone morphometry analysis to evaluate their osteogenic properties. Results: According to scanning electron microscopy, the surface of the titanium flakes had a micro-nano morphology in the WNT group and the KNT and KWNT groups were functionally loaded with kaempferol. In CCK-8 and drug release experiments, the loaded kaempferol and gelatin composite membranes showed no significant toxic effects on cells. The drug release time in the KNT-CG and KWNT-CG groups was significantly longer than that in the KNT and KWNT groups, with the release time in the KWNT-CG group reaching 15 days. In vivo experiments micro-computed tomography and bone morphometry analysis showed that the osteoporosis model had been successfully constructed. The bone volume fraction around the implant increased. Toluidine blue staining showed new bone formation and a significantly increased number of bone trabeculae. Conclusion: Kaempferol micro-nanocomposite coating improved the osseointegration ability of implants in osteoporotic rats.
Keywords: Kaempferol; Osseointegration; Osteoporosis; chitosan; gelatin; implants; micro-nano.
Copyright © 2022 Wang, Yuan, Song, Zang and Yu.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures


References
-
- Bastami F., Paknejad Z., Jafari M., Salehi M., Rezai Rad M., Khojasteh A. (2017). Fabrication of a Three-Dimensional β-tricalcium-phosphate/gelatin Containing Chitosan-Based Nanoparticles for Sustained Release of Bone Morphogenetic Protein-2: Implication for Bone Tissue Engineering. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 72, 481–491. 10.1016/j.msec.2016.10.084 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Elena F., Tomas S., Zbynek S., Monika S., Margit Z., Karel B., et al. (2014). Support for the Initial Attachment, Growth and Differentiation of MG-63 Cells: a Comparison between Nano-Size Hydroxyapatite and Micro-size Hydroxyapatite in Composites. Int. J. Nanomedicine 9, 3687–3706. 10.2147/IJN.S56661 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Gittens R. A., Mclachlan T., Olivares-Navarrete R., Ye C., Berner S., Tannenbaum R., et al. (2011). The Effects of Combined Micron-/submicron-Scale Surface Roughness and Nanoscale Features on Cell Proliferation and Differentiation. Biomaterials 32 (13), 3395–3403. 10.1016/j.biomaterials.2011.01.029 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

