Clinically relevant T cell expansion media activate distinct metabolic programs uncoupled from cellular function
- PMID: 35284590
- PMCID: PMC8897702
- DOI: 10.1016/j.omtm.2022.02.004
Clinically relevant T cell expansion media activate distinct metabolic programs uncoupled from cellular function
Abstract
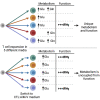
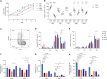
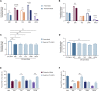
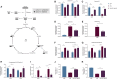
Ex vivo expansion conditions used to generate T cells for immunotherapy are thought to adopt metabolic phenotypes that impede therapeutic efficacy in vivo. The comparison of five different culture media used for clinical T cell expansion revealed unique optima based on different output variables, including proliferation, differentiation, function, activation, and mitochondrial phenotypes. The extent of proliferation and function depended on the culture media rather than stimulation conditions. Moreover, the expanded T cell end products adapted their metabolism when switched to a different media formulation, as shown by glucose and glutamine uptake and patterns of glucose isotope labeling. However, adoption of these metabolic phenotypes was uncoupled to T cell function. Expanded T cell products cultured in ascites from ovarian cancer patients displayed suppressed mitochondrial activity and function irrespective of the ex vivo expansion media. Thus, ex vivo T cell expansion media have profound impacts on metabolism and function.
Keywords: 13C tracer analysis; T cell expansion; cell-based immunotherapy; culture media; metabolism; phenotype.
© 2022 The Authors.
Conflict of interest statement
R.J.D. is a member of the Scientific Advisory Boards of Vida Ventures and Agios Pharmaceuticals and is a founder of Atavistik Biosciences. J.R.C. is an inventor on a patent application for HPLM (PCT/US2017/061,377) assigned to the Whitehead Institute. C.S. is a Principal Scientist at STEMCELL Technologies. J.Y. is a Scientist at STEMCELL Technologies. STEMCELL Technologies provided reagents in kind for the study but were not involved in funding the study, performing experiments, or analyzing the data.
Figures


References
-
- Schubert M.-L., Hoffmann J.-M., Dreger P., Müller-Tidow C., Schmitt M. Chimeric antigen receptor transduced T cells: tuning up for the next generation. Int. J. Cancer. 2018;142:1738–1747. - PubMed
-
- Radvanyi L.G., Bernatchez C., Zhang M., Fox P.S., Miller P., Chacon J., Wu R., Lizee G., Mahoney S., Alvarado G., et al. Specific lymphocyte subsets predict response to adoptive cell therapy using expanded autologous tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes in metastatic melanoma patients. Clin. Cancer Res. Off. J. Am. Assoc. Cancer Res. 2012;18:6758–6770. - PMC - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

