A systematic review of the flood vulnerability using geographic information system
- PMID: 35284686
- PMCID: PMC8914095
- DOI: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2022.e09075
A systematic review of the flood vulnerability using geographic information system
Abstract
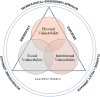
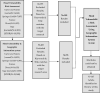
The world has faced many disasters in recent years, but flood impacts have gained immense importance and attention due to their adverse effects. More than half of global flood destruction and damages occur in the Asia region, which causes losses of life, damage infrastructure, and creates panic conditions among the communities. To provide a better understanding of flood hazard management, flood vulnerability assessment is the primary objective. In this case, vulnerability is the central construct in flood analysis and assessment. Many researchers have defined different approaches and methods to understand vulnerability assessment and how geographic information systems assess the flood vulnerability and their associated risk. Geographic information systems track and predict the disaster trend and mitigate the risk and damages. This study systematically reviews the methodologies used to measure floods and their vulnerabilities by integrating geographic information system. Articles on flood vulnerability from 2010 to 2020 were selected and reviewed. Through the systematic review methodology of five research engines, the researchers discovered a difference in flood vulnerability assessment tools and techniques that can be bridged by integrating high-resolution data with a multidimensional vulnerability methodology. The study reviewed several vulnerability components and directly examined the shortcomings in flood vulnerability approaches at different levels. The research contributed that the indicator-based approach gives a better understanding of vulnerability assessment. The geographic information system provides an effective environment for mapping and precise analysis to mitigate the flood disaster.
Keywords: Disaster; Flood vulnerability; Geographic information system.
© 2022 The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Abah R., Clement An application of Geographic Information System in mapping flood risk zones in a north central city in Nigeria. Afr. J. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2013;7(6):365–371.
-
- Abbas S.H., Srivastava R.K., Tiwari R.P., Ramudu P.B. GIS-based disaster management: a case study for Allahabad Sadar sub-district (India) Manag. Environ. Qual. Int. J. 2009;20(1):33–51.
-
- Abid S.K., Sulaiman N., Mahmud N.P.N., Nazir U., Adnan N.A. A review on the application of remote sensing and geographic information system in flood crisis management. J. Crit. Rev. 2020;7(16):491–496.
-
- Abid S.K., Sulaiman N., Wei C.S., U N Flood vulnerability and resilience : exploring the factors that influence flooding in Sarawak Flood vulnerability and resilience : exploring the factors that influence flooding in Sarawak. IOP Conf. Ser. Earth Environ. Sci. 2021;802
-
- Abid Sheikh K., Sulaiman N., Chan S.W., Nazir U., Abid M., Han H., Ariza-Montes A., Vega-Muñoz A. Toward an integrated disaster management approach: how artificial intelligence can boost disaster management. Sustainability. 2021;13(22)
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources