Atypical comorbidities in a child considered to have type 1 diabetes led to the diagnosis of SLC29A3 spectrum disorder
- PMID: 35284993
- PMCID: PMC7613593
- DOI: 10.1007/s42000-022-00352-3
Atypical comorbidities in a child considered to have type 1 diabetes led to the diagnosis of SLC29A3 spectrum disorder
Abstract
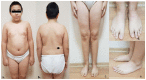
Introduction: SLC29A3 spectrum disorder is an autosomal, recessively inherited, autoinflammatory, multisystem disorder characterized by distinctive cutaneous features, including hyperpigmentation or hypertrichosis, hepatosplenomegaly, hearing loss, cardiac anomalies, hypogonadism, short stature, and insulin-dependent diabetes.
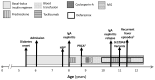
Case presentation: Herein, we report a 6-year-old boy who presented with features resembling type 1 diabetes mellitus, but his clinical course was complicated by IgA nephropathy, pure red cell aplasia, and recurrent febrile episodes. The patient was tested for the presence of pathogenic variants in 53 genes related to monogenic diabetes and found to be compound heterozygous for two SLC29A3 pathogenic variants (p. Arg386Gln and p. Leu298fs).
Conclusion: This case demonstrated that SLC29A3 spectrum disorder should be included in the differential diagnosis of diabetes with atypical comorbidities, even when the distinctive dermatological hallmarks of SLC29A3 spectrum disorder are entirely absent.
Keywords: Anemia; Intravenous immunoglobulin; Monogenic diabetes; Steroid; Tocilizumab.
© 2022. Hellenic Endocrine Society.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest. The Wellcome Trust had no role in the design and conduct of the study; collection, management, analysis, and interpretation of the data; preparation, review, or approval of the manuscript; and decision to submit the manuscript for publication.
Figures
References
-
- Molho-Pessach V, Ramot Y, Camille F, et al. H syndrome: the first 79 patients. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2014;70(1):80–8. - PubMed
-
- Melki I, Lambot K, Jonard L, et al. Mutation in the SLC29A3 gene: a new cause of a monogenic, autoinflammatory condition. Pediatrics. 2013;131(4):e1308-13. - PubMed
-
- Ozlu C, Yesiltepe Mutlu G, Hatun S. A Turkish girl with H syndrome: stunted growth and development of autoimmune insulin dependent diabetes mellitus in the 6th year of diagnosis. J Pediatr Endocrinol Metab. 2019;32(1):89–93. - PubMed
-
- Çağdaş D, Sürücü N, Tan Ç, et al. Autoinflammation in addition to combined immunodeficiency: SLC29A3 gene defect. Mol Immunol. 2020;121:28–37. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Supplementary concepts
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

