Duodenal-jejunal bypass liner for the treatment of type 2 diabetes and obesity: 3-year outcomes in the First National Health Service (NHS) EndoBarrier Service
- PMID: 35285080
- PMCID: PMC9313821
- DOI: 10.1111/dme.14827
Duodenal-jejunal bypass liner for the treatment of type 2 diabetes and obesity: 3-year outcomes in the First National Health Service (NHS) EndoBarrier Service
Conflict of interest statement
None.
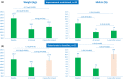
Figures
References
-
- International Diabetes Federation . IDF diabetes atlas, 10th ed. 2021. (accessed 28 December 2021). https://www.diabetesatlas.org/
-
- Ryder REJ, Irwin SP, Burbridge W, et al. The United Kingdom's first NHS Endobarrier service for advanced diabesity: 1‐year outcomes for all 62 treated patients. Br J Diabetes. 2019;19:110‐117. 10.15277/bjd.2019.226 - DOI
-
- Ryder REJ, Yadagiri M, Burbridge W, et al. The United Kingdom’s first NHS EndoBarrier service for long‐standing poorly controlled type 2 diabetes and obesity: outcomes one year after EndoBarrier removal. Br J Diabetes. 2021;21:76‐83. 10.15277/bjd.2021.295 - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

