Valproate utilisation trends among women of childbearing potential in Ireland between 2014 and 2019: A drug utilisation study using interrupted time series
- PMID: 35285110
- PMCID: PMC9315025
- DOI: 10.1002/pds.5427
Valproate utilisation trends among women of childbearing potential in Ireland between 2014 and 2019: A drug utilisation study using interrupted time series
Abstract
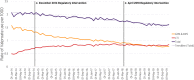
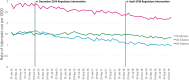
Purpose: This study aimed to examine trends in valproate use among women of childbearing potential (WCBP) aged 16-44 years in Ireland following two European-directed regulatory interventions in December 2014 and April 2018.
Methods: This was a repeated cross-sectional study using monthly national pharmacy claims data, to examine trend changes in the prevalence of valproate use among WCBP pre and post two separate regulatory events in December 2014 and April 2018. Annual population estimates from the Central Statistics Office were used to calculate the prevalence rate per 1000 eligible women. Segmented regression analysis of interrupted time series with negative binomial regression was used to examine rates for WCBP aged 16-44 years, and by 10-year age groups. Prevalence ratios (PR) are presented with 95% confidence intervals (CIs).
Results: Among WCBP aged 16-44 years, there was no statistically significant change in the month-to-month prevalence ratio in the post- compared to pre-December 2014 intervention period. A significant decline was, however, observed in the post-, compared to pre-April 2018 intervention period (PR = 0.998, [95% CIs: 0.996, 1.000]; p = 0.029). Among those aged 16-24 years, a significant decreasing trend in the month-to-month prevalence ratio was found in the post- compared to pre-December 2014 intervention period (PR = 0.991, [95% CIs: 0.984, 0.998];p <0.01). A marginal effect was observed in the post- compared to pre-April 2018 intervention period for those aged 25-34 years (PR = 0.996, [95% CIs: 0.992, 1.000]; p = 0.048).
Conclusion: Although no evidence of change was observed following the December 2014 intervention period, a significant decline in the prevalence ratio of valproate use was observed after the 2018 intervention, which may reflect the introduction of the most recent contraindication measures.
Keywords: European medicines agency; interrupted time series; pregnancy prevention programme; sodium valproate; teratogenicity.
© 2022 The Authors. Pharmacoepidemiology and Drug Safety published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Impact of 2018 EU Risk Minimisation Measures and Revised Pregnancy Prevention Programme on Utilisation and Prescribing Trends of Medicinal Products Containing Valproate: An Interrupted Time Series Study.Drug Saf. 2023 Jul;46(7):689-702. doi: 10.1007/s40264-023-01314-3. Epub 2023 Jun 9. Drug Saf. 2023. PMID: 37294532 Free PMC article.
-
Valproate utilisation trends among girls and women from 2013 to 2018.Seizure. 2019 Aug;70:77-81. doi: 10.1016/j.seizure.2019.07.001. Epub 2019 Jul 4. Seizure. 2019. PMID: 31310965
-
Effectiveness of risk minimisation measures for valproate: A drug utilisation study in Europe.Pharmacoepidemiol Drug Saf. 2021 Mar;30(3):292-303. doi: 10.1002/pds.5166. Epub 2020 Nov 23. Pharmacoepidemiol Drug Saf. 2021. PMID: 33108674 Free PMC article.
-
Valproate in the treatment of epilepsy in girls and women of childbearing potential.Epilepsia. 2015 Jul;56(7):1006-19. doi: 10.1111/epi.13021. Epub 2015 May 16. Epilepsia. 2015. PMID: 25851171 Review.
-
Ethosuximide, sodium valproate or lamotrigine for absence seizures in children and adolescents.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2021 Jan 21;1(1):CD003032. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD003032.pub5. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2021. PMID: 33475151 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
How effective is the implementation of the valproate pregnancy prevention programme in Montenegro? - A 7-year national retrospective study.Ther Adv Drug Saf. 2025 Jul 24;16:20420986251360888. doi: 10.1177/20420986251360888. eCollection 2025. Ther Adv Drug Saf. 2025. PMID: 40727569 Free PMC article.
-
Impact of Risk Minimisation Measures on Valproate Use among Women of Reproductive Age in Latvia Between 2013 and 2020: A 7-Year Nationwide Prescription Database Study.Drugs Real World Outcomes. 2023 Dec;10(4):639-649. doi: 10.1007/s40801-023-00394-y. Epub 2023 Oct 12. Drugs Real World Outcomes. 2023. PMID: 37821776 Free PMC article.
-
Mixed Impact of Direct Healthcare Professional Communications When Considering Proximal Outcomes and the Targeted Population: A Systematic Review.Pharmacoepidemiol Drug Saf. 2025 Mar;34(3):e70135. doi: 10.1002/pds.70135. Pharmacoepidemiol Drug Saf. 2025. PMID: 40122533 Free PMC article.
-
Trends in Prenatal Exposure to Antiseizure Medications Over the Past Decade: A Nationwide Study.Neurology. 2025 Aug 26;105(4):e213933. doi: 10.1212/WNL.0000000000213933. Epub 2025 Jul 23. Neurology. 2025. PMID: 40700674 Free PMC article.
-
Prenatal Exposure to Valproic Acid Across Various Indications for Use.JAMA Netw Open. 2024 May 1;7(5):e2412680. doi: 10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2024.12680. JAMA Netw Open. 2024. PMID: 38776082 Free PMC article.
References
-
- European Medicines Agency . Valproate and related substances. Article‐31 referral ‐ PRAC assessment report 2014. https://www.ema.europa.eu/en/documents/referral/valproate-related-substa... (Accessed 1 June 2021).
-
- Mole TB, Appleton R, Marson A. Withholding the choice of sodium valproate to young women with generalised epilepsy: are we causing more harm than good? Seizure. 2015;24:127‐130. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

