The evolving role of long noncoding RNA HIF1A-AS2 in diabetic retinopathy: a cross-link axis between hypoxia, oxidative stress and angiogenesis via MAPK/VEGF-dependent pathway
- PMID: 35285425
- PMCID: PMC8928809
- DOI: 10.1080/13510002.2022.2050086
The evolving role of long noncoding RNA HIF1A-AS2 in diabetic retinopathy: a cross-link axis between hypoxia, oxidative stress and angiogenesis via MAPK/VEGF-dependent pathway
Abstract
Background: Diabetic retinopathy (DR) signifies a frequent serious diabetic complication influencing retinal structure and function. Dysregulation of lncRNAs drives a wide array of human diseases especially diabetes; thus, we aimed to study lncRNA HIF1A-AS2 role and its interplay with hypoxia, oxidative stress (OS), and angiogenesis in DR.
Materials and methods: 60 DM patients in addition to 15 healthy subjects. were enrolled. LncRNA HIF1A-AS2 mRNA relative gene expression was assessed. Hypoxia inducible factor 1-alpha (HIF-1α), vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF), mitogen activated protein kinase (MAPK), and endoglin levels were assessed. Detection of DNA damage using comet assay, and Redox status parameters were also detected.
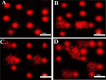
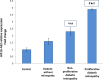
Results: LncRNA HIF1A-AS2 expression was significantly increased in diabetic patients with the highest levels in proliferative DR patients. Moreover, HIFα, VEGF, MAPK, and Endogolin levels were significantly higher in the diabetic patients compared to control group with the highest levels in in proliferative DR patients. Significant DNA damage in comet assay was observed to be the highest in this group.
Conclusion: We observed for the first time the imminent role of long noncoding RNA HIF1A-AS2 in DR throughout its stages and its interplay with hypoxia, OS, and angiogenesis via MAPK/VEGF-dependent pathway.
Keywords: Diabetic retinopathy; HIF-1α; HIF1A-AS2; MAPK; VEGF; angiogenesis; endoglin; oxidative stress.
Conflict of interest statement
No potential conflict of interest was reported by the author(s).
Figures
References
-
- Flaxman SR, Bourne RRA, Resniko S, et al. . Global causes of blindness and distance vision impairment 1990–2020: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Lancet Glob. Health. 2017;5(12):e1221–e1234. - PubMed
-
- Van der Giet M, Henkel C, Schuchardt M, et al. . Anti-VEGF drugs in Eye diseases: local therapy with potential systemic effects. Curr Pharm Des. 2015;21(24):3548–3556. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
