Accessible Hepatitis C Care for People Who Inject Drugs: A Randomized Clinical Trial
- PMID: 35285851
- PMCID: PMC8922207
- DOI: 10.1001/jamainternmed.2022.0170
Accessible Hepatitis C Care for People Who Inject Drugs: A Randomized Clinical Trial
Abstract
Importance: To achieve hepatitis C elimination, treatment programs need to engage, treat, and cure people who inject drugs.
Objective: To compare a low-threshold, nonstigmatizing hepatitis C treatment program that was colocated at a syringe service program (accessible care) with facilitated referral to local clinicians through a patient navigation program (usual care).
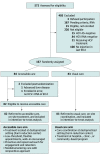
Design, setting, and participants: This single-site randomized clinical trial was conducted at the Lower East Side Harm Reduction Center, a syringe service program in New York, New York, and included 167 participants who were hepatitis C virus RNA-positive and had injected drugs during the prior 90 days. Participants enrolled between July 2017 and March 2020. Data were analyzed after all patients completed 1 year of follow-up (after March 2021).
Interventions: Participants were randomized 1:1 to the accessible care or usual care arm.
Main outcomes and measures: The primary end point was achieving sustained virologic response within 12 months of enrollment.
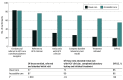
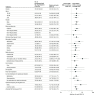
Results: Among the 572 participants screened, 167 (mean [SD] age, 42.0 [10.6] years; 128 (77.6%) male, 36 (21.8%) female, and 1 (0.6) transgender individuals; 8 (4.8%) Black, 97 (58.5%) Hispanic, and 53 (32.1%) White individuals) met eligibility criteria and were enrolled, with 2 excluded postrandomization (n = 165). Baseline characteristics were similar between the 2 arms. In the intention-to-treat analysis, 55 of 82 participants (67.1%) in the accessible care arm and 19 of 83 participants (22.9%) in the usual care arm achieved a sustained virologic response (P < .001). Loss to follow-up (12.2% [accessible care] and 16.9% [usual care]; P = .51) was similar in the 2 arms. Of the participants who received therapy, 55 of 64 (85.9%) and 19 of 22 (86.3%) achieved a sustained virologic response in the accessible care and usual care arms, respectively (P = .96). Significantly more participants in the accessible care arm achieved all steps in the care cascade, with the greatest attrition in the usual care arm seen in referral to hepatitis C virus clinician and attending clinical visit.
Conclusions and relevance: In this randomized clinical trial, among people who inject drugs with hepatitis C infection, significantly higher rates of cure were achieved using the accessible care model that focused on low-threshold, colocated, destigmatized, and flexible hepatitis C care compared with facilitated referral. To achieve hepatitis C elimination, expansion of treatment programs that are specifically geared toward engaging people who inject drugs is paramount.
Trial registration: ClinicalTrials.gov Identifier: NCT03214679.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
Comment in
-
Curing Hepatitis C-Requires More Than a Prescription.JAMA Intern Med. 2022 May 1;182(5):502. doi: 10.1001/jamainternmed.2022.0181. JAMA Intern Med. 2022. PMID: 35285866 No abstract available.
-
Hepatitis C Virus Treatment Delivered via Telemedicine to Persons With Opioid Use Disorder.JAMA Intern Med. 2022 Sep 1;182(9):1011. doi: 10.1001/jamainternmed.2022.2566. JAMA Intern Med. 2022. PMID: 35816336 No abstract available.
References
-
- World Health Organization . Global hepatitis report, 2017. Accessed July 27, 2021. https://www.who.int/publications/i/item/global-hepatitis-report-2017
-
- Biden J. A proclamation on national Hepatitis Testing Day, 2021. Accessed July 21, 2021. https://www.whitehouse.gov/briefing-room/presidential-actions/2021/05/18...
Publication types
MeSH terms
Associated data
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

