Banxia-Houpu decoction diminishes iron toxicity damage in heart induced by chronic intermittent hypoxia
- PMID: 35286247
- PMCID: PMC8928803
- DOI: 10.1080/13880209.2022.2043392
Banxia-Houpu decoction diminishes iron toxicity damage in heart induced by chronic intermittent hypoxia
Abstract
Context: Obstructive sleep apnoea (OSA) causes chronic intermittent hypoxia (CIH), which results in mitochondrial dysfunction and generates reactive oxygen species (ROS) in the heart. Excessive free iron could accelerate oxidative damage, which may be involved in this process. Banxia-Houpu decoction (BHD) was reported to improve the apnoea hypopnoea index in OSA patients, but the specific mechanism was still unclear.
Objective: To investigate whether BHD could reduce CIH-induced heart damage by regulating iron metabolism and mitochondrial function.
Materials and methods: C57BL/6N mice were randomly divided into control, CIH and BHD groups. Mice were exposed to CIH (21 - 5% O2, 20 times/h, 8 h/d) and administered BHD (3.51, 7.01 and 14.02 g/kg, intragastrically) for 21 d. Cardiac and mitochondrial function, iron levels, apoptosis and mitophagy were determined.
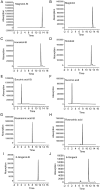
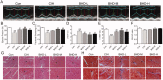
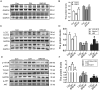
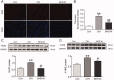
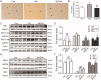
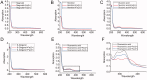
Results: BHD (7.01 g/kg) significantly improved cardiac dysfunction, pathological change and mitochondrial structure induced by CIH. BHD increased the Bcl-2/Bax ratio (1.4-fold) and inhibited caspase 3 cleavage in CIH mice (0.45-fold). BHD activated mitophagy by upregulating Parkin (1.94-fold) and PINK1 (1.26-fold), inhibiting the PI3K-AKT-mTOR pathway. BHD suppressed ROS generation by decreasing NOX2 (0.59-fold) and 4-HNE (0.83-fold). BHD reduced the total iron in myocardial cells (0.72-fold) and mitochondrial iron by downregulating Mfrn2 (0.81-fold) and MtFt (0.78-fold) proteins, and upregulating ABCB8 protein (1.33-fold). Rosmarinic acid, the main component of Perilla Leaf in BHD, was able to react with Fe2+ and Fe3+ in vitro.
Discussion and conclusions: These findings encourage the use of BHD to resist cardiovascular injury and provide the theoretical basis for clinical treatment in OSA patients.
Keywords: Obstructive sleep apnoea; cardiac damage; mitochondrial disfunction; rosmarinic acid.
Conflict of interest statement
No potential conflict of interest was reported by the author(s).
Figures


References
-
- An JR, Zhao YS, Luo LF, Guan P, Tan M, Ji ES.. 2020. Huperzine A, reduces brain iron overload and alleviates cognitive deficit in mice exposed to chronic intermittent hypoxia. Life Sci. 250:117573–10. - PubMed
-
- Ban T, Ishihara T, Kohno H, Saita S, Ichimura A, Maenaka K, Oka T, Mihara K, Ishihara N.. 2017. Molecular basis of selective mitochondrial fusion by heterotypic action between OPA1 and cardiolipin. Nat Cell Biol. 19(7):856–863. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
