Characterization of the WRKY gene family in Akebia trifoliata and their response to Colletotrichum acutatum
- PMID: 35287589
- PMCID: PMC8919620
- DOI: 10.1186/s12870-022-03511-1
Characterization of the WRKY gene family in Akebia trifoliata and their response to Colletotrichum acutatum
Abstract
Background: Akebia trifoliata, belonging to the Lardizabalaceae family, is a well-known Chinese traditional medicinal plant, susceptible to many diseases, such as anthracnose and powdery mildew. WRKY is one of the largest plant-specific transcription factor families and plays important roles in plant growth, development and stress response, especially in disease resistance. However, little was known about the numbers, characters, evolutionary relationship and expression of WRKY genes in A. trifoliata in response to plant disease due to lacking of A. trifoliata genome.
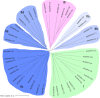
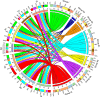
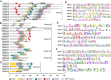
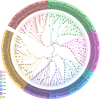
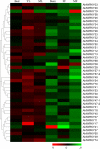
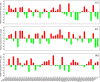
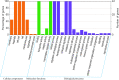
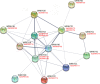
Results: A total of 42 putative AktWRKY genes were identified based on the full-length transcriptome-sequencing data of A. trifoliata. Then 42 AktWRKY genes were divided into three major groups (Group I-III) based on the WRKY domains. Motif analysis showed members within same group shared a similar motif composition, implying a functional conservation. Tissue-specific expression analysis showed that AktWRKY genes could be detected in all tissues, while few AktWRKY genes were tissue specific. We further evaluated the expression of AktWRKY genes in three varieties in response to Colletotrichum acutatum by qRT-PCR. The expression patterns of AktWRKY genes were similar between C01 and susceptible variety I02, but distinctly different in resistant variety H05. In addition, it showed that more than 64 percentages of AktWRKY genes were differentially expressed during fungal infection in I02 and H05. Furthermore, Gene ontology (GO) analysis showed that AktWRKY genes were categorized into 26 functional groups under cellular components, molecular functions and biological processes, and a predicted protein interaction network was also constructed.
Conclusions: Results of bioinformation analysis and expression patterns implied that AktWRKYs might play multiple function in response to biotic stresses. Our study could facilitate to further investigate the function and regulatory mechanism of the WRKY in A. trifoliata during pathogen response.
Keywords: Akebia trifoliata; Colletotrichum acutatum; WRKY transcription factors; biotic stress.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures

References
-
- Chen L, Song Y, Li S, Zhang L, Zou C, Yu D. The role of WRKY transcription factors in plant abiotic stresses. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2012;1819(2):120–128. - PubMed
-
- Rushton DL, Tripathi P, Rabara RC, Lin J, Ringler P, Boken AK, Langum TJ, Smidt L, Boomsma DD, Emme NJ, et al. WRKY transcription factors: key components in abscisic acid signalling. Plant Biotechnol J. 2012;10(1):2–11. - PubMed
-
- Eulgem T, Rushton PJ, Robatzek S, Somssich IE. The WRKY superfamily of plant transcription factors. Trends Plant Sci. 2000;5(5):199–206. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Supplementary concepts
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

