CELF1 promotes matrix metalloproteinases gene expression at transcriptional level in lens epithelial cells
- PMID: 35287612
- PMCID: PMC8922852
- DOI: 10.1186/s12886-022-02344-8
CELF1 promotes matrix metalloproteinases gene expression at transcriptional level in lens epithelial cells
Abstract
Background: RNA binding proteins (RBPs)-mediated regulation plays important roles in many eye diseases, including the canonical RBP CELF1 in cataract. While the definite molecular regulatory mechanisms of CELF1 on cataract still remain elusive.
Methods: In this study, we overexpressed CELF1 in human cultured lens epithelial SRA01/04 cells and applied whole transcriptome sequencing (RNA-seq) method to analyze the global differences mediated by CELF1. We then analyzed public RNA-seq and CELF1-RNA interactome data to decipher the underlying mechanisms.
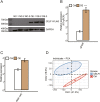
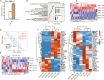
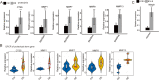
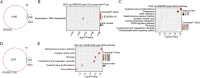
Results: The results showed that transcriptome profile was globally changed by CELF1 overexpression (CELF1-OE). Functional analysis revealed CELF1 specifically increased the expression of genes in extracellular matrix disassembly, extracellular matrix organization, and proteolysis, which could be classified into matrix metalloproteinases (MMPs) family. This finding was also validated by RT-qPCR and public mouse early embryonic lens data. Integrating analysis with public CELF1-RNA interactome data revealed that no obvious CELF1-binding peak was found on the transcripts of these genes, indicating an indirectly regulatory role of CELF1 in lens epithelial cells.
Conclusions: Our study demonstrated that CELF1-OE promotes transcriptional level of MMP genes; and this regulation may be completed by other ways except for binding to RNA targets. These results suggest that CELF1-OE is implicated in the development of lens, which is associated with cataract and expands our understanding of CELF1 regulatory roles as an RNA binding protein.
Keywords: CELF1; Cataract; MMPs; RNA-seq; Transcriptional regulation.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures

References
-
- Thompson J, Lakhani N. Cataracts. Prim Care. 2015;42(3):409–423. - PubMed
-
- Khokhar S, Pillay G, Agarwal E. Pediatric Cataract - Importance of Early Detection and Management. Indian J Pediatr. 2018;85(3):209–216. - PubMed
-
- Liu YC, Wilkins M, Kim T, Malyugin B, Mehta JS. Cataracts. Lancet 2017;390(10094):600–12. - PubMed
-
- Mitchell SF, Parker R. Principles and properties of eukaryotic mRNPs. Molecular cell. 2014;54(4):547–558. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

