Combined Liver, Pancreas-Duodenum, and Kidney Transplantation for Patients with Hepatitis B Cirrhosis, Uremia, and Insulin-Dependent Diabetes
- PMID: 35288528
- PMCID: PMC8934010
- DOI: 10.12659/AOT.935860
Combined Liver, Pancreas-Duodenum, and Kidney Transplantation for Patients with Hepatitis B Cirrhosis, Uremia, and Insulin-Dependent Diabetes
Abstract
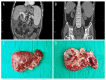
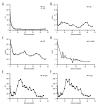
BACKGROUND Abdominal organ cluster transplantation for the treatment of upper abdominal end-stage diseases is a serious conundrum for surgeons. CASE REPORT We performed clinical assessment of quadruple organ transplantation (liver, pancreas, duodenum, and kidney) for a patient with end-stage liver disease, post-chronic hepatitis B cirrhosis, uremia, and insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus, and explored the optimal surgical procedure. Simultaneous classic orthotopic liver, pancreas-duodenum, and heterotopic renal transplantation was performed on a 46-year-old man. The process was an improvement of surgery implemented with a single vascular anastomosis (Y graft of the superior mesenteric artery and the celiac artery open together in the common iliac artery). The pancreatic secretions and bile were drained through a modified uncut jejunal loop anastomosis, and the donor's kidneys were placed in the right iliac fossa. The patient was prescribed basiliximab, glucocorticoid, tacrolimus, and mycophenolate mofetil for immunosuppression. The hepatic function recovered satisfactorily on postoperative day (POD) 3, and pancreatic function recovered satisfactorily in postoperative month (POM) 1. Hydronephrosis occurred in the transplanted kidney, with elevated creatinine on POD 15. Consequently, renal pelvic puncture and drainage were performed. His creatinine dropped to a normal level on POD 42. No allograft rejections or other complications, like pancreatic leakage, thrombosis, or localized infections, occurred. The patient had normal liver, renal, and pancreas functions with insulin-independent after POD 365. CONCLUSIONS Simultaneous classic orthotopic liver, pancreas-duodenum, and heterotopic renal transplantation is a promising therapeutic option for patients with insulin-dependent diabetes combined with end-stage hepatic and renal disease, and our center's experience can provide a reference for clinical multiorgan transplantation.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures

Similar articles
-
[A case report of simultaneous liver, pancreas-duodenum, and kidney transplantation in a patient with post-hepatitic cirrhosis combined with uremia and insulin-dependent diabetes related to chronic pancreatitis].Zhonghua Yi Xue Za Zhi. 2006 Sep 12;86(34):2421-4. Zhonghua Yi Xue Za Zhi. 2006. PMID: 17156656 Chinese.
-
Simultaneous liver, pancreas-duodenum and kidney transplantation in a patient with hepatitis B cirrhosis, uremia and insulin dependent diabetes mellitus.World J Gastroenterol. 2017 Dec 7;23(45):8104-8108. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v23.i45.8104. World J Gastroenterol. 2017. PMID: 29259387 Free PMC article.
-
A 14-Year Follow-Up of a Combined Liver-Pancreas-Kidney Transplantation: Case Report and Literature Review.Front Med (Lausanne). 2020 Apr 28;7:148. doi: 10.3389/fmed.2020.00148. eCollection 2020. Front Med (Lausanne). 2020. PMID: 32411713 Free PMC article.
-
Current state of combined kidney and pancreas transplantation.Blood Purif. 2011;31(1-3):96-101. doi: 10.1159/000321865. Epub 2011 Jan 10. Blood Purif. 2011. PMID: 21228575 Review.
-
Diagnosis, management, and outcome of late duodenal complications in portal-enteric pancreas transplantation: case reports.J Am Coll Surg. 1997 Dec;185(6):560-6. doi: 10.1016/s1072-7515(97)00110-5. J Am Coll Surg. 1997. PMID: 9404880 Review.
Cited by
-
Screening and identification of HTNVpv entry inhibitors with high-throughput pseudovirus-based chemiluminescence.Virol Sin. 2022 Aug;37(4):531-537. doi: 10.1016/j.virs.2022.04.015. Epub 2022 May 2. Virol Sin. 2022. PMID: 35513270 Free PMC article.
-
A novel risk model based on anoikis: Predicting prognosis and immune infiltration in cutaneous melanoma.Front Pharmacol. 2023 Jan 16;13:1090857. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2022.1090857. eCollection 2022. Front Pharmacol. 2023. PMID: 36726781 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Yu LX, Liu XY, Xu J, et al. Clinical evaluation of abdominal multiorgan transplantation. Di Yi Jun Yi Da Xue Xue Bao. 2004;24(2):148–51. - PubMed
-
- Xu J, Yu LX, Deng WF, et al. [Simultaneous liver-pancreas-duodenum transplantation: One case report and review of the literature]. Zhonghua Wai Ke Za Zhi. 2006;44(3):157–60. [in Chinese] - PubMed
-
- John PR, Thuluvath PJ. Outcome of liver transplantation in patients with diabetes mellitus: A case-control study. Hepatology. 2001;34(5):889–95. - PubMed
-
- Nakache R, Merhav H. Rapid en bloc liver-pancreas-kidney procurement: More pancreas with better vascular supply. Transplant Proc. 2000;32(4):755–56. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

