Mechanisms of innate and adaptive immunity to the Pfizer-BioNTech BNT162b2 vaccine
- PMID: 35288714
- PMCID: PMC8989677
- DOI: 10.1038/s41590-022-01163-9
Mechanisms of innate and adaptive immunity to the Pfizer-BioNTech BNT162b2 vaccine
Abstract
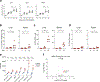
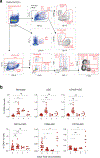
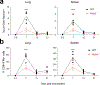
Despite the success of the BNT162b2 mRNA vaccine, the immunological mechanisms that underlie its efficacy are poorly understood. Here we analyzed the innate and adaptive responses to BNT162b2 in mice, and show that immunization stimulated potent antibody and antigen-specific T cell responses, as well as strikingly enhanced innate responses after secondary immunization, which was concurrent with enhanced serum interferon (IFN)-γ levels 1 d following secondary immunization. Notably, we found that natural killer cells and CD8+ T cells in the draining lymph nodes are the major producers of this circulating IFN-γ. Analysis of knockout mice revealed that induction of antibody and T cell responses to BNT162b2 was not dependent on signaling via Toll-like receptors 2, 3, 4, 5 and 7 nor inflammasome activation, nor the necroptosis or pyroptosis cell death pathways. Rather, the CD8+ T cell response induced by BNT162b2 was dependent on type I interferon-dependent MDA5 signaling. These results provide insights into the molecular mechanisms by which the BNT162b2 vaccine stimulates immune responses.
© 2022. The Author(s), under exclusive licence to Springer Nature America, Inc.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing Interests Statement
Bali Pulendran has served or is serving on the External Immunology Network of GSK, and on the scientific advisory board of Sanofi, Medicago, CircBio, Boehringer-Ingelheim. A.D.G. is a visiting scientist at Genentech, Inc. Other authors have declared no competing interests.
Figures




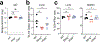








Comment in
-
Making innate sense of mRNA vaccine adjuvanticity.Nat Immunol. 2022 Apr;23(4):474-476. doi: 10.1038/s41590-022-01168-4. Nat Immunol. 2022. PMID: 35354958 No abstract available.
References
-
- Kariko K, Buckstein M, Ni H & Weissman D Suppression of RNA recognition by Toll-like receptors: the impact of nucleoside modification and the evolutionary origin of RNA. Immunity 23, 165–175 (2005). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

